Introduction: The Future of Skin Cancer Diagnosis is Here
Every year, millions of people worldwide receive a skin cancer diagnosis, making it one of the most common forms of cancer globally. Early detection is critical—studies show that up to 86% of melanomas can be prevented through timely identification and intervention. However, there’s a significant problem: there simply aren’t enough experienced dermatologists to meet the growing demand for accurate, rapid skin lesion assessment.
Enter RemixFormer++, a revolutionary artificial intelligence system that promises to transform how we detect and diagnose skin tumors. Developed by researchers from Alibaba’s DAMO Academy and Xiangya Hospital, this multi-modal transformer model doesn’t just analyze a single image—it mimics the comprehensive diagnostic approach of expert dermatologists by simultaneously processing clinical photographs, high-resolution dermoscopy images, and patient medical history.
The results are remarkable: RemixFormer++ achieves an overall classification accuracy of 92.6% across 12 different skin tumor types, performing on par with or better than 191 professional dermatologists in comprehensive clinical trials. This isn’t just incremental improvement—it represents a fundamental leap forward in AI-assisted medical diagnosis.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how RemixFormer++ works, why its multi-modal approach matters, and what this breakthrough means for the future of dermatological care.
Understanding the Challenge: Why Skin Tumor Diagnosis is So Difficult
The Complexity of Visual Diagnosis
Diagnosing skin tumors accurately presents unique challenges that even experienced dermatologists find demanding. Malignant and benign lesions often share ambiguous and confusing visual characteristics, making differentiation extremely difficult based on appearance alone.
Key diagnostic challenges include:
- Visual similarity between dangerous melanomas and harmless moles
- Variations in lighting, angle, and image quality in clinical photographs
- Fine-grained textural patterns in dermoscopy that require specialized training to interpret
- The need to correlate visual findings with patient history and risk factors
Traditional AI approaches have attempted to solve this problem by analyzing single image types, but this fundamentally contradicts how real dermatologists work. A competent physician doesn’t make diagnoses based solely on one photograph—they combine multiple information sources to reach accurate conclusions.
The Multi-Modal Diagnostic Process
When a dermatologist examines a patient, they follow a structured multi-modal assessment protocol:
| Diagnostic Stage | Information Type | Key Features Examined |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Inspection | Macroscopic photos | Lesion location, shape, color, size |
| Dermoscopy | Magnified images | Pigment networks, globules, vascular structures |
| Medical History | Patient metadata | Age, sun exposure, evolution patterns, symptoms |
| Final Diagnosis | Integrated analysis | Synthesis of all available information |
Bold Takeaway: RemixFormer++ is the first AI system to fully replicate this comprehensive diagnostic workflow, processing all three data modalities simultaneously through specialized neural network branches.
The RemixFormer++ Architecture: A Technical Deep Dive
Three Specialized Branches for Complete Analysis
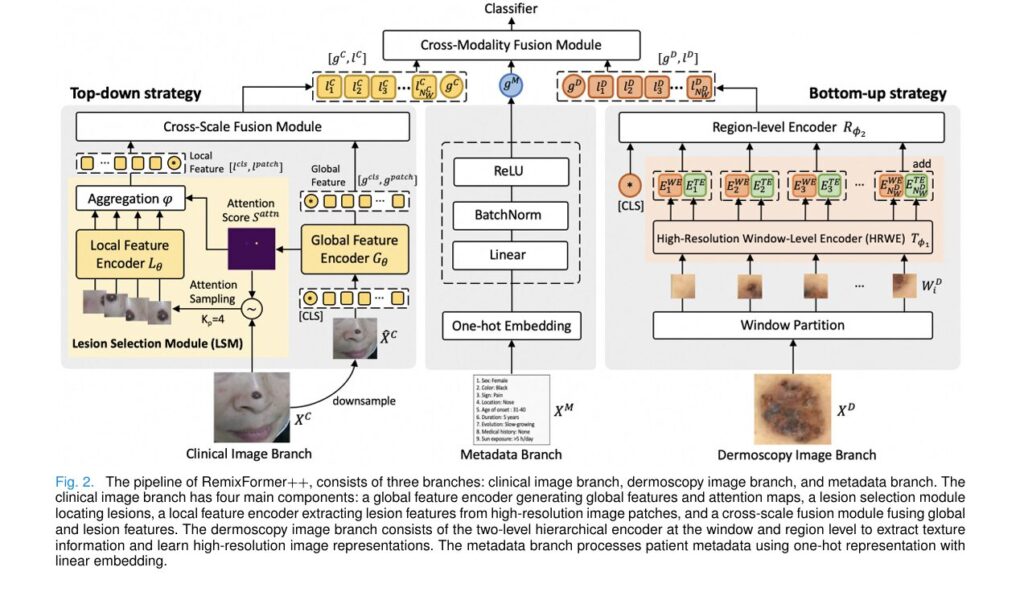
RemixFormer++ employs a sophisticated three-branch architecture, with each branch optimized for processing a specific type of diagnostic information. This design philosophy directly mirrors how expert dermatologists cognitively process different data types using distinct mental strategies.
Branch 1: Clinical Image Processing with Top-Down Attention
The clinical image branch handles standard photographs taken with digital cameras or smartphones. These images capture the global context of skin lesions—their location on the body, overall shape, and relationship to surrounding tissue.
How Top-Down Attention Works:
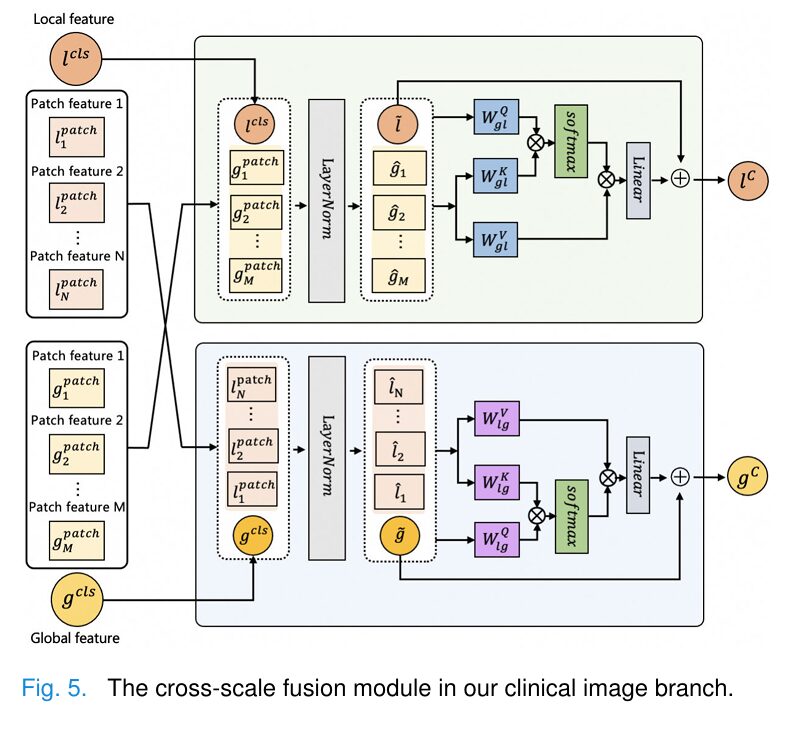
When humans examine clinical images, we naturally employ a top-down visual strategy: first taking in the whole scene, then focusing attention on specific areas of interest. RemixFormer++ replicates this through its innovative Lesion Selection Module (LSM).
The mathematical foundation involves computing attention scores between a special classification token and image patches:
$$S^{attn} = \frac{1}{H} \sum_{h=1}^{H} \text{SoftMax}(O_1^h) \odot \text{SoftMax}(O_2^h)$$Where H represents the number of attention heads, and the bidirectional attention scores identify which image regions most likely contain lesions.
Key Innovation: The LSM uses differentiable attention sampling to overcome the non-differentiability of discrete patch selection, enabling end-to-end training:
$$\phi = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{v \in V} L_\theta([l^{cls}, l^{patch}])$$This allows the network to learn which regions are diagnostically important without requiring pixel-level annotations.
Branch 2: Dermoscopy Analysis with Bottom-Up Hierarchical Encoding
Dermoscopy images present a fundamentally different challenge. These specialized photographs use optical magnification and illumination to reveal subsurface skin structures invisible to the naked eye. Dermatologists examine dermoscopy images by searching for specific textural patterns—pigment networks, globules, regression structures—that indicate particular disease types.
The Two-Level Hierarchical Architecture:
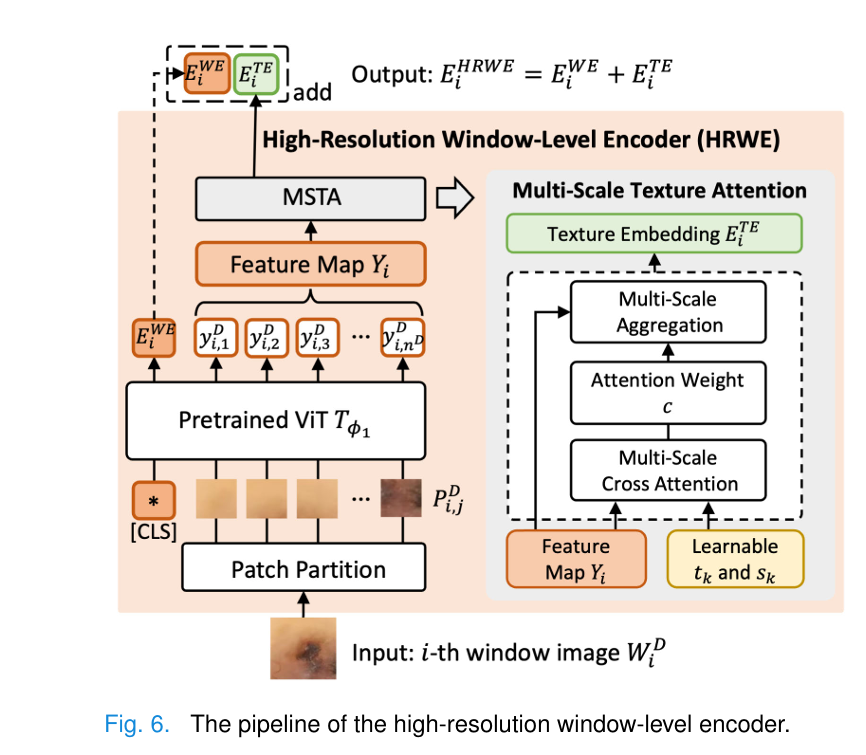
RemixFormer++ processes high-resolution dermoscopy images (up to 2048×2048 pixels) through an ingenious two-level system:
- Window-Level Encoder (HRWE): Processes 256×256 pixel windows using a Vision Transformer pre-trained with self-supervised learning
- Region-Level Encoder: Aggregates window embeddings to capture global context and inter-window relationships
Multi-Scale Texture Attention (MSTA):
A critical innovation is the learnable texture template system that captures important dermoscopic patterns:
$$a_{j,k} = y_{i,j} \cdot (t_k)^T$$ $$c_{j,k} = \frac{\exp(-s_k a_{j,k})}{\sum_{\ell=1}^{K_s} \exp(-s_\ell a_{j,\ell})}$$Here, tk represents learnable texture templates (analogous to the pattern recognition stored in a dermatologist’s long-term memory), while sk provides multi-scale attention weighting.
The final texture embedding aggregates information across all patches:
$$E_{i,k}^{TE} = \sum_{j=1}^{n^D} c_{j,k} \cdot y_{i,j}$$Bold Takeaway: The MSTA module effectively learns to recognize 32 distinct textural patterns automatically, without requiring explicit labeling of dermoscopic features during training.
Branch 3: Metadata Integration for Clinical Context
The metadata branch processes nine critical patient attributes using one-hot encoding:
- Demographics: Sex, skin color
- Symptoms: Pain, itching, bleeding
- Location: Body site of the lesion
- Temporal factors: Age of onset, duration, evolution pattern
- Risk factors: Medical history, sun exposure time
Research demonstrates that metadata dramatically improves diagnostic accuracy. For instance, prolonged sun exposure strongly correlates with actinic keratosis, while rapidly growing lesions warrant higher suspicion for malignancy.
Cross-Modality Fusion: Bringing It All Together
The magic happens in the Cross-Modality Fusion (CMF) module, which combines features from all three branches using sophisticated cross-attention mechanisms:
$$Q^g = \tilde{g}W_{lg}^Q, \quad K^g = \hat{l}W_{lg}^K, \quad V^g = \hat{l}W_{lg}^V$$ $$M_{cross}^g = \text{softmax}\left(\frac{Q^g(K^g)^T}{\sqrt{F/h}}\right) \cdot V^g$$This bidirectional attention allows global features to inform local analysis and vice versa, creating a rich, integrated representation for final classification.
Performance Results: Matching Expert Dermatologists
Benchmark Performance Across Multiple Datasets
RemixFormer++ was validated on several prestigious datasets, consistently achieving state-of-the-art results:
| Dataset | Modality | Accuracy | F1 Score | Key Achievement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAD-UFES-20 | Clinical + Metadata | 81.3% | — | +11.2% over previous best |
| ISIC 2018 | Dermoscopy | 94.1% | 87.0% | +1.5% BMCA improvement |
| ISIC 2019 | Dermoscopy | 91.2% | 72.0% | +6.3% BMCA improvement |
| Derm7pt | All modalities | 82.5% | 66.6% | +5.3% F1 over prior work |
| X-SkinTumor-12 | All modalities | 92.6% | 82.4% | New benchmark |
Reader Study: AI vs. 191 Dermatologists
The most compelling validation came from a comprehensive reader study comparing RemixFormer++ against 191 dermatologists across four expertise levels:
- Dermatology specialists (58 physicians)
- Attending dermatologists (59 physicians)
- Dermatology residents (49 physicians)
- General practitioners (25 physicians)
Key Findings:
- RemixFormer++ outperformed the average performance of all physician groups when using multi-modal data
- The AI achieved an AUC of 0.971 on the 100-patient test set
- Even top-performing specialists were matched by the algorithm
- Importantly, junior physicians benefited most from AI assistance, as they had less experience interpreting dermoscopy
Clinical Implications and Real-World Applications
Democratizing Expert-Level Diagnosis
One of the most profound implications of RemixFormer++ is its potential to democratize access to expert-level skin cancer screening. In many regions, especially rural and underserved areas, access to dermatology specialists is severely limited. An AI system capable of matching specialist-level performance could:
- Enable primary care physicians to confidently triage skin lesions
- Support teledermatology initiatives in remote locations
- Reduce diagnostic delays that currently cost lives
- Alleviate workload on overburdened dermatology departments
Memory-Efficient Design for Practical Deployment
Unlike many AI systems that require expensive specialized hardware, RemixFormer++ was designed with memory efficiency as a core principle:
| Configuration | Image Resolution | GPU Memory | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical branch | 512×512 | 1,265 MiB | Standard GPUs |
| Dermoscopy branch | 2048×2048 | 1,809 MiB | Clinical deployment |
| Full model | Mixed | <4 GB | Edge devices |
This efficiency enables deployment in real clinical environments without requiring expensive computational infrastructure.
Limitations and Ethical Considerations
Current Limitations
While RemixFormer++ represents a significant advance, important limitations remain:
- Dataset bias: Training data may not represent all skin types equally
- Edge cases: Rare tumor types with limited training examples remain challenging
- Interpretability: Deep learning decisions can be difficult to explain to patients
- Regulatory approval: Clinical deployment requires extensive validation and approval
Ethical AI in Healthcare
The researchers emphasize that RemixFormer++ is designed to augment, not replace, human expertise. Responsible deployment requires:
- Transparent communication with patients about AI involvement
- Maintaining physician oversight of all diagnostic decisions
- Continuous monitoring of system performance across diverse populations
- Regular retraining as new data becomes available
Conclusion: A New Era in AI-Assisted Dermatology
RemixFormer++ represents a watershed moment in medical AI—demonstrating that thoughtfully designed multi-modal systems can match or exceed human expert performance on complex diagnostic tasks. By faithfully replicating the comprehensive assessment workflow of experienced dermatologists, this system achieves accuracy levels that seemed unattainable just a few years ago.
The implications extend far beyond dermatology. The architectural innovations pioneered here—top-down attention for global context, bottom-up hierarchical encoding for fine-grained analysis, and sophisticated cross-modality fusion—provide a template for AI systems addressing similarly complex diagnostic challenges in radiology, pathology, and other medical specialties.
As this technology matures and gains regulatory approval, we may soon see a future where expert-level skin cancer screening is available to anyone with a smartphone camera—potentially saving countless lives through earlier detection of deadly melanomas.
Take Action: Stay Informed About AI in Healthcare
The rapid advancement of AI in medical diagnosis affects us all. Here’s how you can stay engaged:
- Share this article with friends and family to raise awareness about AI-assisted diagnosis
- Subscribe to our newsletter for updates on breakthrough medical AI developments
- Discuss with your healthcare provider how AI tools might enhance your care
- Support research funding for responsible AI development in healthcare
Have questions about AI in dermatology or want to share your experiences? Leave a comment below—we read and respond to every message!
Here is the comprehensive implementation of the RemixFormer++ model based on the research paper.
# =============================================================================
# CROSS-MODALITY FUSION MODULE (CMF)
# =============================================================================
class CrossModalityFusion(nn.Module):
"""
Cross-Modality Fusion (CMF) Module.
This module fuses features from clinical images, dermoscopy images,
and metadata using attention-based mechanisms to create a unified
representation for classification.
"""
def __init__(
self,
clinical_dim: int,
dermoscopy_dim: int,
metadata_dim: int,
fusion_dim: int = 512,
num_heads: int = 8,
dropout: float = 0.1
):
super().__init__()
self.fusion_dim = fusion_dim
# Project all modalities to same dimension
self.clinical_proj = nn.Linear(clinical_dim, fusion_dim)
self.dermoscopy_proj = nn.Linear(dermoscopy_dim, fusion_dim)
self.metadata_proj = nn.Linear(metadata_dim, fusion_dim)
# Layer normalization
self.norm_c = nn.LayerNorm(fusion_dim)
self.norm_d = nn.LayerNorm(fusion_dim)
self.norm_m = nn.LayerNorm(fusion_dim)
# Multi-head cross-attention for fusion
self.cross_attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(
embed_dim=fusion_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
dropout=dropout,
batch_first=True
)
# Self-attention for final fusion
self.self_attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(
embed_dim=fusion_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
dropout=dropout,
batch_first=True
)
# MLP for final representation
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(fusion_dim * 3, fusion_dim),
nn.LayerNorm(fusion_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(fusion_dim, fusion_dim)
)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(
self,
clinical_feat: Tensor,
dermoscopy_feat: Tensor,
metadata_feat: Optional[Tensor] = None,
clinical_local: Optional[Tensor] = None,
dermoscopy_local: Optional[Tensor] = None
) -> Tensor:
"""
Forward pass for Cross-Modality Fusion.
Args:
clinical_feat: Clinical global feature (B, clinical_dim)
dermoscopy_feat: Dermoscopy global feature (B, dermoscopy_dim)
metadata_feat: Optional metadata feature (B, metadata_dim)
clinical_local: Optional clinical local features (B, N_c, clinical_dim)
dermoscopy_local: Optional dermoscopy local features (B, N_d, dermoscopy_dim)
Returns:
Fused feature for classification (B, fusion_dim)
"""
B = clinical_feat.shape[0]
# Project to fusion dimension
c_feat = self.clinical_proj(clinical_feat) # (B, fusion_dim)
d_feat = self.dermoscopy_proj(dermoscopy_feat) # (B, fusion_dim)
# Normalize
c_feat = self.norm_c(c_feat)
d_feat = self.norm_d(d_feat)
# Handle metadata
if metadata_feat is not None:
m_feat = self.metadata_proj(metadata_feat)
m_feat = self.norm_m(m_feat)
# Stack features as sequence for attention
features = torch.stack([c_feat, d_feat, m_feat], dim=1) # (B, 3, fusion_dim)
else:
features = torch.stack([c_feat, d_feat], dim=1) # (B, 2, fusion_dim)
# Self-attention over modalities
fused, _ = self.self_attention(features, features, features)
fused = self.dropout(fused)
fused = fused + features # Residual connection
# Flatten and process through MLP
fused_flat = fused.view(B, -1)
# Pad if only 2 modalities
if metadata_feat is None:
fused_flat = F.pad(fused_flat, (0, self.fusion_dim))
output = self.mlp(fused_flat)
return output
# =============================================================================
# REMIXFORMER++ COMPLETE MODEL
# =============================================================================
class RemixFormerPlusPlus(nn.Module):
"""
RemixFormer++: A Multi-Modal Transformer Model for Precision Skin Tumor
Differential Diagnosis With Memory-Efficient Attention.
This is the complete model that integrates:
1. Clinical Image Branch (top-down architecture)
2. Dermoscopy Image Branch (bottom-up architecture)
3. Metadata Branch (one-hot encoding + MLP)
4. Cross-Modality Fusion (CMF) for final classification
Reference: Xu et al., IEEE TMI 2025
"""
def __init__(
self,
num_classes: int = 12,
# Clinical branch parameters
clinical_img_size_hr: int = 896,
clinical_img_size_global: int = 384,
clinical_img_size_local: int = 224,
clinical_embed_dim: int = 96,
clinical_depths: List[int] = [2, 2, 6, 2],
clinical_num_heads: List[int] = [3, 6, 12, 24],
clinical_window_size: int = 7,
num_lesion_patches: int = 4,
# Dermoscopy branch parameters
dermoscopy_img_size: int = 1024,
dermoscopy_window_size: int = 256,
dermoscopy_patch_size: int = 16,
dermoscopy_embed_dim: int = 384,
dermoscopy_hrwe_depth: int = 12,
dermoscopy_region_depth: int = 4,
dermoscopy_num_heads: int = 6,
num_textures: int = 32,
# Metadata branch parameters
metadata_dims: Optional[List[int]] = None,
metadata_hidden_dim: int = 256,
# Fusion parameters
fusion_dim: int = 512,
fusion_num_heads: int = 8,
# Common parameters
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1,
dropout: float = 0.1
):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.clinical_img_size_hr = clinical_img_size_hr
self.dermoscopy_img_size = dermoscopy_img_size
# Compute feature dimensions
self.clinical_feat_dim = int(clinical_embed_dim * 2 ** (len(clinical_depths) - 1))
self.dermoscopy_feat_dim = dermoscopy_embed_dim
# Default metadata dimensions for X-SkinTumor-12 dataset (9 attributes)
if metadata_dims is None:
# [Sex, Color, Sign, Location, Age of onset, Duration, Evolution, Medical history, Sun exposure]
metadata_dims = [2, 5, 4, 6, 5, 3, 4, 3, 3]
self.metadata_dims = metadata_dims
self.metadata_total_dim = sum(metadata_dims)
# ===================== Clinical Image Branch =====================
self.clinical_branch = ClinicalImageBranch(
img_size_global=clinical_img_size_global,
img_size_local=clinical_img_size_local,
patch_size=4,
in_chans=3,
embed_dim=clinical_embed_dim,
depths=clinical_depths,
num_heads=clinical_num_heads,
window_size=clinical_window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
num_lesion_patches=num_lesion_patches,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate
)
# ===================== Dermoscopy Image Branch =====================
self.dermoscopy_branch = DermoscopyImageBranch(
img_size=dermoscopy_img_size,
window_size=dermoscopy_window_size,
patch_size=dermoscopy_patch_size,
in_chans=3,
embed_dim=dermoscopy_embed_dim,
hrwe_depth=dermoscopy_hrwe_depth,
region_depth=dermoscopy_region_depth,
num_heads=dermoscopy_num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
num_textures=num_textures,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate
)
# ===================== Metadata Branch =====================
self.metadata_branch = MetadataBranch(
metadata_dims=metadata_dims,
embed_dim=fusion_dim,
hidden_dim=metadata_hidden_dim,
dropout=dropout
)
# ===================== Cross-Modality Fusion =====================
self.cmf = CrossModalityFusion(
clinical_dim=self.clinical_feat_dim,
dermoscopy_dim=self.dermoscopy_feat_dim,
metadata_dim=fusion_dim,
fusion_dim=fusion_dim,
num_heads=fusion_num_heads,
dropout=dropout
)
# ===================== Classification Head =====================
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(fusion_dim, fusion_dim),
nn.LayerNorm(fusion_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(fusion_dim, num_classes)
)
# Initialize weights
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m: nn.Module):
"""Initialize weights for the model."""
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm1d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(
self,
clinical_image: Optional[Tensor] = None,
dermoscopy_image: Optional[Tensor] = None,
metadata: Optional[Tensor] = None,
return_attention: bool = False
) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for RemixFormer++.
Args:
clinical_image: Clinical image tensor (B, 3, H, W)
dermoscopy_image: Dermoscopy image tensor (B, 3, H, W)
metadata: One-hot encoded metadata (B, total_metadata_dim)
return_attention: Whether to return attention maps
Returns:
Dictionary containing:
- 'logits': Classification logits (B, num_classes)
- 'clinical_attn': Clinical attention map (if return_attention=True)
- 'features': Fused features before classification
"""
outputs = {}
# Process available modalities
clinical_global = None
clinical_local = None
clinical_attn = None
dermoscopy_global = None
dermoscopy_local = None
metadata_feat = None
# ===================== Clinical Image Branch =====================
if clinical_image is not None:
# Resize to high-resolution input size
if clinical_image.shape[2] != self.clinical_img_size_hr:
clinical_image = F.interpolate(
clinical_image,
size=(self.clinical_img_size_hr, self.clinical_img_size_hr),
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=False
)
clinical_global, clinical_local, clinical_attn = self.clinical_branch(clinical_image)
if return_attention:
outputs['clinical_attn'] = clinical_attn
# ===================== Dermoscopy Image Branch =====================
if dermoscopy_image is not None:
# Resize to expected input size
if dermoscopy_image.shape[2] != self.dermoscopy_img_size:
dermoscopy_image = F.interpolate(
dermoscopy_image,
size=(self.dermoscopy_img_size, self.dermoscopy_img_size),
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=False
)
dermoscopy_global, dermoscopy_local = self.dermoscopy_branch(dermoscopy_image)
# ===================== Metadata Branch =====================
if metadata is not None:
metadata_feat = self.metadata_branch(metadata)
# ===================== Handle Missing Modalities =====================
B = self._get_batch_size(clinical_image, dermoscopy_image, metadata)
device = self._get_device(clinical_image, dermoscopy_image, metadata)
if clinical_global is None:
clinical_global = torch.zeros(B, self.clinical_feat_dim, device=device)
if dermoscopy_global is None:
dermoscopy_global = torch.zeros(B, self.dermoscopy_feat_dim, device=device)
# ===================== Cross-Modality Fusion =====================
fused_features = self.cmf(
clinical_feat=clinical_global,
dermoscopy_feat=dermoscopy_global,
metadata_feat=metadata_feat,
clinical_local=clinical_local,
dermoscopy_local=dermoscopy_local
)
outputs['features'] = fused_features
# ===================== Classification =====================
logits = self.classifier(fused_features)
outputs['logits'] = logits
return outputs
def _get_batch_size(self, *tensors) -> int:
"""Get batch size from available tensors."""
for t in tensors:
if t is not None:
return t.shape[0]
raise ValueError("At least one input tensor must be provided")
def _get_device(self, *tensors) -> torch.device:
"""Get device from available tensors."""
for t in tensors:
if t is not None:
return t.device
return torch.device('cpu')
def forward_clinical_only(self, clinical_image: Tensor) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
"""Forward pass using only clinical images."""
return self.forward(clinical_image=clinical_image)
def forward_dermoscopy_only(self, dermoscopy_image: Tensor) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
"""Forward pass using only dermoscopy images."""
return self.forward(dermoscopy_image=dermoscopy_image)
def forward_cd(
self,
clinical_image: Tensor,
dermoscopy_image: Tensor
) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
"""Forward pass using clinical and dermoscopy images (CD mode)."""
return self.forward(
clinical_image=clinical_image,
dermoscopy_image=dermoscopy_image
)
def forward_cdm(
self,
clinical_image: Tensor,
dermoscopy_image: Tensor,
metadata: Tensor
) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
"""Forward pass using all three modalities (CDM mode)."""
return self.forward(
clinical_image=clinical_image,
dermoscopy_image=dermoscopy_image,
metadata=metadata
)
# =============================================================================
# MODEL CONFIGURATIONS
# =============================================================================
def remixformer_tiny(num_classes: int = 12, **kwargs) -> RemixFormerPlusPlus:
"""
RemixFormer++ Tiny configuration.
Suitable for limited GPU memory or faster training.
"""
return RemixFormerPlusPlus(
num_classes=num_classes,
clinical_embed_dim=64,
clinical_depths=[2, 2, 4, 2],
clinical_num_heads=[2, 4, 8, 16],
dermoscopy_embed_dim=256,
dermoscopy_hrwe_depth=8,
dermoscopy_region_depth=3,
dermoscopy_num_heads=4,
fusion_dim=384,
**kwargs
)
def remixformer_small(num_classes: int = 12, **kwargs) -> RemixFormerPlusPlus:
"""
RemixFormer++ Small configuration.
Good balance between performance and efficiency.
"""
return RemixFormerPlusPlus(
num_classes=num_classes,
clinical_embed_dim=96,
clinical_depths=[2, 2, 6, 2],
clinical_num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24],
dermoscopy_embed_dim=384,
dermoscopy_hrwe_depth=12,
dermoscopy_region_depth=4,
dermoscopy_num_heads=6,
fusion_dim=512,
**kwargs
)
def remixformer_base(num_classes: int = 12, **kwargs) -> RemixFormerPlusPlus:
"""
RemixFormer++ Base configuration.
Standard configuration as described in the paper.
"""
return RemixFormerPlusPlus(
num_classes=num_classes,
clinical_embed_dim=96,
clinical_depths=[2, 2, 6, 2],
clinical_num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24],
clinical_window_size=7,
num_lesion_patches=4,
dermoscopy_embed_dim=384,
dermoscopy_hrwe_depth=12,
dermoscopy_region_depth=4,
dermoscopy_num_heads=6,
num_textures=32,
fusion_dim=512,
**kwargs
)
# =============================================================================
# LOSS FUNCTIONS
# =============================================================================
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
"""Focal Loss for handling class imbalance in skin tumor datasets."""
def __init__(
self,
alpha: Optional[Tensor] = None,
gamma: float = 2.0,
reduction: str = 'mean'
):
super().__init__()
self.alpha = alpha
self.gamma = gamma
self.reduction = reduction
def forward(self, inputs: Tensor, targets: Tensor) -> Tensor:
ce_loss = F.cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='none', weight=self.alpha)
pt = torch.exp(-ce_loss)
focal_loss = ((1 - pt) ** self.gamma) * ce_loss
if self.reduction == 'mean':
return focal_loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == 'sum':
return focal_loss.sum()
return focal_loss
class LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(nn.Module):
"""Cross-entropy loss with label smoothing."""
def __init__(self, smoothing: float = 0.1):
super().__init__()
self.smoothing = smoothing
def forward(self, inputs: Tensor, targets: Tensor) -> Tensor:
n_classes = inputs.shape[-1]
log_preds = F.log_softmax(inputs, dim=-1)
loss = -log_preds.sum(dim=-1)
nll_loss = F.nll_loss(log_preds, targets, reduction='none')
smooth_loss = loss / n_classes
return (1 - self.smoothing) * nll_loss.mean() + self.smoothing * smooth_loss.mean()
# =============================================================================
# DATA PREPROCESSING AND AUGMENTATION
# =============================================================================
class SkinLesionTransforms:
"""
Data augmentation transforms for skin lesion images.
Implements the augmentation pipeline described in the paper.
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_size: int = 896,
is_training: bool = True,
normalize_mean: List[float] = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
normalize_std: List[float] = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
):
self.img_size = img_size
self.is_training = is_training
self.normalize_mean = normalize_mean
self.normalize_std = normalize_std
def __call__(self, image: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Apply transforms to image.
Note: This is a simplified version. In practice, use torchvision.transforms
or albumentations for more robust augmentation.
"""
if self.is_training:
# Random horizontal flip (50% probability)
if torch.rand(1).item() > 0.5:
image = torch.flip(image, dims=[-1])
# Random vertical flip (50% probability)
if torch.rand(1).item() > 0.5:
image = torch.flip(image, dims=[-2])
# Color jittering (brightness, contrast, saturation)
if torch.rand(1).item() > 0.5:
brightness_factor = 0.5 + torch.rand(1).item()
image = image * brightness_factor
image = torch.clamp(image, 0, 1)
# Normalize
mean = torch.tensor(self.normalize_mean).view(3, 1, 1)
std = torch.tensor(self.normalize_std).view(3, 1, 1)
image = (image - mean.to(image.device)) / std.to(image.device)
return image
def encode_metadata(
metadata_dict: Dict[str, int],
metadata_dims: List[int]
) -> Tensor:
"""
Encode metadata attributes as one-hot vectors.
Args:
metadata_dict: Dictionary of attribute values
metadata_dims: List of dimensions for each attribute
Returns:
One-hot encoded tensor
"""
encoded = []
attribute_names = [
'sex', 'color', 'sign', 'location', 'age_of_onset',
'duration', 'evolution', 'medical_history', 'sun_exposure'
]
for i, (name, dim) in enumerate(zip(attribute_names, metadata_dims)):
one_hot = torch.zeros(dim)
if name in metadata_dict:
idx = min(metadata_dict[name], dim - 1)
one_hot[idx] = 1.0
encoded.append(one_hot)
return torch.cat(encoded)
# =============================================================================
# TRAINING UTILITIES
# =============================================================================
class AverageMeter:
"""Computes and stores the average and current value."""
def __init__(self):
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.val = 0
self.avg = 0
self.sum = 0
self.count = 0
def update(self, val: float, n: int = 1):
self.val = val
self.sum += val * n
self.count += n
self.avg = self.sum / self.count
def compute_metrics(
predictions: Tensor,
targets: Tensor,
num_classes: int
) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""
Compute classification metrics.
Returns:
Dictionary with accuracy, balanced accuracy, precision, recall, F1
"""
preds = predictions.argmax(dim=1)
correct = (preds == targets).float()
accuracy = correct.mean().item()
# Per-class metrics
class_correct = torch.zeros(num_classes)
class_total = torch.zeros(num_classes)
class_pred_total = torch.zeros(num_classes)
for c in range(num_classes):
class_mask = targets == c
pred_mask = preds == c
class_correct[c] = ((preds == c) & (targets == c)).sum().float()
class_total[c] = class_mask.sum().float()
class_pred_total[c] = pred_mask.sum().float()
# Sensitivity (Recall) per class
sensitivity = class_correct / (class_total + 1e-8)
# Precision per class
precision = class_correct / (class_pred_total + 1e-8)
# F1 per class
f1 = 2 * (precision * sensitivity) / (precision + sensitivity + 1e-8)
# Balanced accuracy
balanced_acc = sensitivity.mean().item()
# Macro F1
macro_f1 = f1.mean().item()
return {
'accuracy': accuracy,
'balanced_accuracy': balanced_acc,
'macro_precision': precision.mean().item(),
'macro_sensitivity': sensitivity.mean().item(),
'macro_f1': macro_f1
}
def train_one_epoch(
model: RemixFormerPlusPlus,
train_loader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,
criterion: nn.Module,
device: torch.device,
epoch: int,
scheduler: Optional[torch.optim.lr_scheduler._LRScheduler] = None
) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""
Train the model for one epoch.
Args:
model: RemixFormer++ model
train_loader: Training data loader
optimizer: Optimizer
criterion: Loss function
device: Device to use
epoch: Current epoch number
scheduler: Optional learning rate scheduler
Returns:
Dictionary with training metrics
"""
model.train()
loss_meter = AverageMeter()
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
# Extract batch data (adjust based on your dataloader)
clinical_images = batch.get('clinical_image')
dermoscopy_images = batch.get('dermoscopy_image')
metadata = batch.get('metadata')
targets = batch['label'].to(device)
# Move to device
if clinical_images is not None:
clinical_images = clinical_images.to(device)
if dermoscopy_images is not None:
dermoscopy_images = dermoscopy_images.to(device)
if metadata is not None:
metadata = metadata.to(device)
# Forward pass
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(
clinical_image=clinical_images,
dermoscopy_image=dermoscopy_images,
metadata=metadata
)
# Compute loss
loss = criterion(outputs['logits'], targets)
# Backward pass
loss.backward()
# Gradient clipping
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
if scheduler is not None:
scheduler.step()
loss_meter.update(loss.item(), targets.size(0))
if batch_idx % 50 == 0:
print(f'Epoch [{epoch}][{batch_idx}/{len(train_loader)}] '
f'Loss: {loss_meter.avg:.4f}')
return {'train_loss': loss_meter.avg}
@torch.no_grad()
def validate(
model: RemixFormerPlusPlus,
val_loader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
criterion: nn.Module,
device: torch.device,
num_classes: int
) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""
Validate the model.
Returns:
Dictionary with validation metrics
"""
model.eval()
loss_meter = AverageMeter()
all_preds = []
all_targets = []
for batch in val_loader:
clinical_images = batch.get('clinical_image')
dermoscopy_images = batch.get('dermoscopy_image')
metadata = batch.get('metadata')
targets = batch['label'].to(device)
if clinical_images is not None:
clinical_images = clinical_images.to(device)
if dermoscopy_images is not None:
dermoscopy_images = dermoscopy_images.to(device)
if metadata is not None:
metadata = metadata.to(device)
outputs = model(
clinical_image=clinical_images,
dermoscopy_image=dermoscopy_images,
metadata=metadata
)
loss = criterion(outputs['logits'], targets)
loss_meter.update(loss.item(), targets.size(0))
all_preds.append(outputs['logits'].cpu())
all_targets.append(targets.cpu())
all_preds = torch.cat(all_preds, dim=0)
all_targets = torch.cat(all_targets, dim=0)
metrics = compute_metrics(all_preds, all_targets, num_classes)
metrics['val_loss'] = loss_meter.avg
return metrics
# =============================================================================
# EXAMPLE USAGE AND TESTING
# =============================================================================
def test_model():
"""Test the RemixFormer++ model with random inputs."""
print("=" * 60)
print("Testing RemixFormer++ Model")
print("=" * 60)
# Create model
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f"\nUsing device: {device}")
model = remixformer_small(num_classes=12).to(device)
# Count parameters
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
trainable_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
print(f"Total parameters: {total_params:,}")
print(f"Trainable parameters: {trainable_params:,}")
# Test with different modality combinations
batch_size = 2
# Test 1: Clinical image only
print("\n" + "-" * 40)
print("Test 1: Clinical Image Only (C)")
clinical_img = torch.randn(batch_size, 3, 896, 896).to(device)
outputs = model.forward_clinical_only(clinical_img)
print(f" Input shape: {clinical_img.shape}")
print(f" Output logits shape: {outputs['logits'].shape}")
print(f" Output features shape: {outputs['features'].shape}")
# Test 2: Dermoscopy image only
print("\n" + "-" * 40)
print("Test 2: Dermoscopy Image Only (D)")
dermoscopy_img = torch.randn(batch_size, 3, 1024, 1024).to(device)
outputs = model.forward_dermoscopy_only(dermoscopy_img)
print(f" Input shape: {dermoscopy_img.shape}")
print(f" Output logits shape: {outputs['logits'].shape}")
# Test 3: Clinical + Dermoscopy (CD)
print("\n" + "-" * 40)
print("Test 3: Clinical + Dermoscopy (CD)")
outputs = model.forward_cd(clinical_img, dermoscopy_img)
print(f" Output logits shape: {outputs['logits'].shape}")
# Test 4: Full model CDM
print("\n" + "-" * 40)
print("Test 4: Clinical + Dermoscopy + Metadata (CDM)")
metadata = torch.randn(batch_size, 35).to(device) # 35 = sum of metadata_dims
outputs = model.forward_cdm(clinical_img, dermoscopy_img, metadata)
print(f" Metadata shape: {metadata.shape}")
print(f" Output logits shape: {outputs['logits'].shape}")
# Test 5: With attention maps
print("\n" + "-" * 40)
print("Test 5: With Attention Maps")
outputs = model(
clinical_image=clinical_img,
dermoscopy_image=dermoscopy_img,
metadata=metadata,
return_attention=True
)
if 'clinical_attn' in outputs:
print(f" Clinical attention shape: {outputs['clinical_attn'].shape}")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("All tests passed successfully!")
print("=" * 60)
return model
def example_training_loop():
"""Example training loop for RemixFormer++."""
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("Example Training Configuration")
print("=" * 60)
# Configuration
config = {
'num_classes': 12,
'batch_size': 4,
'learning_rate': 1e-4,
'weight_decay': 0.05,
'epochs': 200,
'warmup_epochs': 10,
}
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# Create model
model = remixformer_base(num_classes=config['num_classes']).to(device)
# Optimizer (AdamW as commonly used for transformers)
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(
model.parameters(),
lr=config['learning_rate'],
weight_decay=config['weight_decay'],
betas=(0.9, 0.999)
)
# Learning rate scheduler (cosine annealing)
# Note: In practice, use with actual data loader length
# scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(
# optimizer, T_max=config['epochs'], eta_min=1e-6
# )
# Loss function
criterion = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(smoothing=0.1)
print(f"\nModel: RemixFormer++ Base")
print(f"Optimizer: AdamW (lr={config['learning_rate']}, wd={config['weight_decay']})")
print(f"Loss: Label Smoothing Cross Entropy (smoothing=0.1)")
print(f"Scheduler: Cosine Annealing")
print(f"Total epochs: {config['epochs']}")
# Example forward pass
print("\nRunning example forward pass...")
batch = {
'clinical_image': torch.randn(config['batch_size'], 3, 896, 896).to(device),
'dermoscopy_image': torch.randn(config['batch_size'], 3, 1024, 1024).to(device),
'metadata': torch.randn(config['batch_size'], 35).to(device),
'label': torch.randint(0, config['num_classes'], (config['batch_size'],)).to(device)
}
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(
clinical_image=batch['clinical_image'],
dermoscopy_image=batch['dermoscopy_image'],
metadata=batch['metadata']
)
loss = criterion(outputs['logits'], batch['label'])
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f" Loss: {loss.item():.4f}")
print(f" Predictions shape: {outputs['logits'].shape}")
print("\nTraining setup complete!")
return model, optimizer, criterion
# =============================================================================
# MAIN ENTRY POINT
# =============================================================================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Run tests
model = test_model()
# Show example training configuration
model, optimizer, criterion = example_training_loop()
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("RemixFormer++ Implementation Complete!")
print("=" * 60)
print("\nUsage examples:")
print(" 1. model = remixformer_small(num_classes=12)")
print(" 2. model = remixformer_base(num_classes=12)")
print(" 3. outputs = model(clinical_image=img_c, dermoscopy_image=img_d, metadata=meta)")
print(" 4. logits = outputs['logits']")
print("=" * 60) return g_out, l_out
# =============================================================================
# CLINICAL IMAGE BRANCH
# =============================================================================
class ClinicalImageBranch(nn.Module):
"""
Clinical Image Branch with top-down architecture.
This branch processes clinical images through:
1. Global Feature Encoder (Gθ) - extracts global context from downsampled images
2. Lesion Selection Module (LSM) - identifies and extracts lesion patches
3. Local Feature Encoder (Lθ) - extracts fine-grained lesion features
4. Cross-Scale Fusion (CSF) - fuses global and local features
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_size_global: int = 384,
img_size_local: int = 224,
patch_size: int = 4,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 96,
depths: List[int] = [2, 2, 6, 2],
num_heads: List[int] = [3, 6, 12, 24],
window_size: int = 7,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
num_lesion_patches: int = 4,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1
):
super().__init__()
self.img_size_global = img_size_global
self.img_size_local = img_size_local
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (len(depths) - 1))
# Global Feature Encoder
self.global_encoder = GlobalFeatureEncoder(
img_size=img_size_global,
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
depths=depths,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate
)
# Lesion Selection Module
feature_map_size = img_size_global // (patch_size * (2 ** (len(depths) - 1)))
self.lsm = LesionSelectionModule(
num_patches=num_lesion_patches,
patch_size=img_size_local,
feature_map_size=feature_map_size,
window_size=window_size
)
# Local Feature Encoder (shares first 3 stages with global encoder)
self.local_encoder = LocalFeatureEncoder(
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
depths=depths,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate,
shared_stages=self.global_encoder.stages
)
# Cross-Scale Fusion Module
self.csf = CrossScaleFusion(
dim=self.num_features,
num_heads=num_heads[-1]
)
# Feature aggregation for multiple local patches
self.local_aggregation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(self.num_features * num_lesion_patches, self.num_features),
nn.LayerNorm(self.num_features),
nn.GELU()
)
def forward(self, x_hr: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Clinical Image Branch.
Args:
x_hr: High-resolution clinical image (B, C, H, W)
Returns:
Tuple of (global feature, local feature, attention map)
"""
B = x_hr.shape[0]
# Downsample for global encoder
x_global = F.interpolate(
x_hr, size=(self.img_size_global, self.img_size_global),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=False
)
# Extract global features and attention scores
g_cls, g_patch, attn_scores = self.global_encoder(x_global)
# Compute feature map dimensions
H = W = self.img_size_global // (4 * 8) # After patch embed and 3 downsamplings
# Select lesion patches using LSM
lesion_patches, attn_map = self.lsm(x_hr, attn_scores, H, W)
# Extract local features from lesion patches
l_cls, l_patch = self.local_encoder(lesion_patches)
# Aggregate local features from multiple patches
l_cls_agg = l_cls.view(B, -1) # (B, Kp * dim)
l_cls_agg = self.local_aggregation(l_cls_agg) # (B, dim)
# Cross-scale fusion
g_C, l_C = self.csf(g_cls, g_patch, l_cls, l_patch)
return g_C, l_C, attn_map
# =============================================================================
# VISION TRANSFORMER (ViT) FOR HRWE
# =============================================================================
class ViTAttention(nn.Module):
"""Standard multi-head self-attention for ViT."""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
num_heads: int = 8,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
attn_drop: float = 0.,
proj_drop: float = 0.
):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
qkv = qkv.permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
q = q * self.scale
attn = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)
attn = F.softmax(attn, dim=-1)
attn_weights = attn
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x, attn_weights
class ViTBlock(nn.Module):
"""Vision Transformer block."""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
num_heads: int,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop: float = 0.,
attn_drop: float = 0.,
drop_path: float = 0.,
act_layer: nn.Module = nn.GELU,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm
):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = ViTAttention(dim, num_heads, qkv_bias, attn_drop, drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
attn_out, attn_weights = self.attn(self.norm1(x))
x = x + self.drop_path(attn_out)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x, attn_weights
class ViTEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
Vision Transformer encoder for window-level feature extraction.
This is used as Tφ1 in the High-Resolution Window-Level Encoder (HRWE).
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_size: int = 256,
patch_size: int = 16,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 384,
depth: int = 12,
num_heads: int = 6,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm
):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_patches = (img_size // patch_size) ** 2
# Patch embedding
self.patch_embed = nn.Conv2d(
in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size
)
# CLS token and position embeddings
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, self.num_patches + 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# Stochastic depth
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, depth)]
# Transformer blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
ViTBlock(
dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[i], norm_layer=norm_layer
)
for i in range(depth)
])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
# Initialize weights
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=.02)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=.02)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass.
Args:
x: Input tensor of shape (B, C, H, W)
Returns:
Tuple of (CLS token embedding, patch embeddings)
"""
B = x.shape[0]
# Patch embedding
x = self.patch_embed(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # (B, num_patches, embed_dim)
# Add CLS token
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(B, -1, -1)
x = torch.cat([cls_tokens, x], dim=1)
# Add position embedding
x = x + self.pos_embed
x = self.pos_drop(x)
# Process through transformer blocks
for blk in self.blocks:
x, _ = blk(x)
x = self.norm(x)
# Separate CLS token and patch embeddings
cls_embed = x[:, 0] # (B, embed_dim)
patch_embed = x[:, 1:] # (B, num_patches, embed_dim)
return cls_embed, patch_embed
# =============================================================================
# MULTI-SCALE TEXTURE ATTENTION (MSTA)
# =============================================================================
class MultiScaleTextureAttention(nn.Module):
"""
Multi-Scale Texture Attention (MSTA) module.
This module learns texture templates that capture important dermoscopic
patterns like pigment networks, globules, and streaks. It implements
Equations 15-16 from the paper.
Key components:
- Learnable texture templates {tk}
- Learnable scaling factors {sk} for multi-scale attention
- Cross-attention between patch embeddings and texture templates
"""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
num_textures: int = 32,
proj_dim: Optional[int] = None
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_textures = num_textures # Ks in the paper
self.proj_dim = proj_dim or dim
# Learnable texture templates (Eq. 15)
self.texture_templates = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(num_textures, dim))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.texture_templates, std=.02)
# Learnable scaling factors for multi-scale attention
self.scale_factors = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(num_textures))
# Output projection
self.proj = nn.Linear(num_textures * dim, self.proj_dim)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(self.proj_dim)
def forward(self, patch_embeddings: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Forward pass for MSTA.
Args:
patch_embeddings: Patch embeddings from ViT (B, n_patches, dim)
Returns:
Texture embedding (B, proj_dim)
"""
B, N, D = patch_embeddings.shape
# Compute attention scores (Eq. 15)
# a_{j,k} = y_{i,j} · t_k^T
attention = torch.einsum('bnd,kd->bnk', patch_embeddings, self.texture_templates)
# Apply learnable scaling and softmax
# c_{j,k} = exp(-s_k * a_{j,k}) / sum_l exp(-s_l * a_{j,l})
scaled_attention = -self.scale_factors.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) * attention
attention_weights = F.softmax(scaled_attention, dim=-1) # (B, N, Ks)
# Compute texture embeddings (Eq. 16)
# E^{TE}_{i,k} = sum_j c_{j,k} * y_{i,j}
texture_features = torch.einsum(
'bnk,bnd->bkd', attention_weights, patch_embeddings
) # (B, Ks, D)
# Concatenate and project
texture_features = texture_features.view(B, -1) # (B, Ks * D)
texture_embedding = self.proj(texture_features) # (B, proj_dim)
texture_embedding = self.norm(texture_embedding)
return texture_embedding
# =============================================================================
# HIGH-RESOLUTION WINDOW-LEVEL ENCODER (HRWE)
# =============================================================================
class HighResolutionWindowLevelEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
High-Resolution Window-Level Encoder (HRWE) Tφ1.
This encoder processes high-resolution dermoscopy image windows using
a self-supervised pre-trained ViT and extracts both window embeddings
and texture embeddings using MSTA.
Output: E^{HRWE}_i = E^{WE}_i + E^{TE}_i (Eq. 17)
"""
def __init__(
self,
window_size: int = 256,
patch_size: int = 16,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 384,
depth: int = 12,
num_heads: int = 6,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
num_textures: int = 32,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1
):
super().__init__()
self.window_size = window_size
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
# ViT encoder (can be initialized with SSL pre-trained weights)
self.vit_encoder = ViTEncoder(
img_size=window_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
depth=depth,
num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate
)
# Multi-Scale Texture Attention
self.msta = MultiScaleTextureAttention(
dim=embed_dim,
num_textures=num_textures,
proj_dim=embed_dim
)
def forward(self, windows: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Forward pass for HRWE.
Args:
windows: Window images (B*N_W, C, window_size, window_size)
Returns:
Combined window and texture embeddings (B*N_W, embed_dim)
"""
# Extract window embedding (CLS token) and patch embeddings
window_embedding, patch_embeddings = self.vit_encoder(windows)
# Extract texture embedding using MSTA
texture_embedding = self.msta(patch_embeddings)
# Combine embeddings (Eq. 17)
hrwe_embedding = window_embedding + texture_embedding
return hrwe_embedding
# =============================================================================
# REGION-LEVEL ENCODER (Rφ2)
# =============================================================================
class RegionLevelEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
Region-Level Encoder (Rφ2) for dermoscopy images.
This encoder takes window-level embeddings from HRWE and learns
global context and dependencies among all windows using transformer
blocks.
"""
def __init__(
self,
embed_dim: int = 384,
depth: int = 4,
num_heads: int = 6,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm
):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
# Learnable CLS token for region-level
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=.02)
# Position embeddings will be created dynamically based on number of windows
self.pos_embed = None
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# Stochastic depth
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, depth)]
# Transformer blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
ViTBlock(
dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[i], norm_layer=norm_layer
)
for i in range(depth)
])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
def _get_pos_embed(self, num_windows: int, device: torch.device) -> Tensor:
"""Get or create position embeddings for the given number of windows."""
if self.pos_embed is None or self.pos_embed.shape[1] != num_windows + 1:
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros(1, num_windows + 1, self.embed_dim, device=device)
)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=.02)
return self.pos_embed
def forward(self, window_embeddings: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Region-Level Encoder.
Args:
window_embeddings: Window embeddings from HRWE (B, N_W, embed_dim)
Returns:
Tuple of (global feature g^D, local features l^D)
"""
B, N_W, D = window_embeddings.shape
# Add CLS token
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(B, -1, -1)
x = torch.cat([cls_tokens, window_embeddings], dim=1) # (B, N_W+1, D)
# Add position embeddings
pos_embed = self._get_pos_embed(N_W, x.device)
if pos_embed.shape[1] == x.shape[1]:
x = x + pos_embed
x = self.pos_drop(x)
# Process through transformer blocks
for blk in self.blocks:
x, _ = blk(x)
x = self.norm(x)
# Separate global and local features
g_D = x[:, 0] # (B, D)
l_D = x[:, 1:] # (B, N_W, D)
return g_D, l_D
# =============================================================================
# DERMOSCOPY IMAGE BRANCH
# =============================================================================
class DermoscopyImageBranch(nn.Module):
"""
Dermoscopy Image Branch with bottom-up architecture.
This branch implements the two-level hierarchical architecture:
1. High-Resolution Window-Level Encoder (HRWE) - processes individual windows
2. Region-Level Encoder - aggregates window information for global context
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_size: int = 1024,
window_size: int = 256,
patch_size: int = 16,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 384,
hrwe_depth: int = 12,
region_depth: int = 4,
num_heads: int = 6,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
num_textures: int = 32,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1
):
super().__init__()
self.img_size = img_size
self.window_size = window_size
self.num_windows = (img_size // window_size) ** 2
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
# High-Resolution Window-Level Encoder (Tφ1)
self.hrwe = HighResolutionWindowLevelEncoder(
window_size=window_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
depth=hrwe_depth,
num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
num_textures=num_textures,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate
)
# Region-Level Encoder (Rφ2)
self.region_encoder = RegionLevelEncoder(
embed_dim=embed_dim,
depth=region_depth,
num_heads=num_heads,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
attn_drop_rate=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path_rate=drop_path_rate
)
def partition_windows(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Partition image into non-overlapping windows.
Args:
x: Input image (B, C, H, W)
Returns:
Windows (B * N_W, C, window_size, window_size)
"""
B, C, H, W = x.shape
assert H % self.window_size == 0 and W % self.window_size == 0, \
f"Image size ({H}x{W}) must be divisible by window size ({self.window_size})"
nH = H // self.window_size
nW = W // self.window_size
# Reshape to (B, nH, window_size, nW, window_size, C)
x = x.view(B, C, nH, self.window_size, nW, self.window_size)
# Permute to (B, nH, nW, C, window_size, window_size)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 4, 1, 3, 5).contiguous()
# Reshape to (B * nH * nW, C, window_size, window_size)
windows = x.view(-1, C, self.window_size, self.window_size)
return windows, nH * nW
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Dermoscopy Image Branch.
Args:
x: Input dermoscopy image (B, C, H, W)
Returns:
Tuple of (global feature g^D, local features l^D)
"""
B = x.shape[0]
# Resize if necessary
if x.shape[2] != self.img_size or x.shape[3] != self.img_size:
x = F.interpolate(x, size=(self.img_size, self.img_size),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# Partition into windows
windows, num_windows = self.partition_windows(x) # (B*N_W, C, ws, ws)
# Process windows through HRWE
window_embeddings = self.hrwe(windows) # (B*N_W, embed_dim)
# Reshape to batch format
window_embeddings = window_embeddings.view(B, num_windows, -1) # (B, N_W, embed_dim)
# Process through Region-Level Encoder
g_D, l_D = self.region_encoder(window_embeddings)
return g_D, l_D
# =============================================================================
# METADATA BRANCH
# =============================================================================
class MetadataBranch(nn.Module):
"""
Metadata Branch for processing patient clinical information.
This branch uses one-hot encoding for categorical metadata attributes
and processes them through a simple MLP to generate metadata embeddings.
"""
def __init__(
self,
metadata_dims: List[int],
embed_dim: int = 384,
hidden_dim: int = 256,
dropout: float = 0.1
):
"""
Args:
metadata_dims: List of dimensions for each metadata attribute
(e.g., [2, 5, 4, 6, 5, 3, 4, 3, 3] for 9 attributes)
embed_dim: Output embedding dimension
hidden_dim: Hidden layer dimension
"""
super().__init__()
self.metadata_dims = metadata_dims
self.total_dim = sum(metadata_dims)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
# Metadata encoder (Mθ in the paper)
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(self.total_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.BatchNorm1d(hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, embed_dim),
nn.BatchNorm1d(embed_dim),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, metadata: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""
Forward pass for Metadata Branch.
Args:
metadata: One-hot encoded metadata (B, total_dim)
Returns:
Metadata embedding g^M (B, embed_dim)
"""
return self.encoder(metadata)"""
RemixFormer++: A Multi-Modal Transformer Model for Precision Skin Tumor
Differential Diagnosis With Memory-Efficient Attention
Complete PyTorch implementation based on the IEEE TMI 2025 paper.
Author: Implementation based on Xu et al. (2025)
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import Tensor
from typing import Optional, Tuple, List, Dict
import math
from functools import partial
from einops import rearrange, repeat
from einops.layers.torch import Rearrange
# =============================================================================
# UTILITY FUNCTIONS AND HELPERS
# =============================================================================
def drop_path(x: Tensor, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False) -> Tensor:
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample for residual blocks."""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_()
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample."""
def __init__(self, drop_prob: float = 0.):
super().__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
def window_partition(x: Tensor, window_size: int) -> Tensor:
"""
Partition feature map into non-overlapping windows.
Args:
x: Input tensor of shape (B, H, W, C)
window_size: Size of each window
Returns:
Windows tensor of shape (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
return windows
def window_reverse(windows: Tensor, window_size: int, H: int, W: int) -> Tensor:
"""
Reverse window partition operation.
Args:
windows: Windows tensor of shape (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
window_size: Size of each window
H, W: Original height and width
Returns:
Tensor of shape (B, H, W, C)
"""
B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))
x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)
return x
# =============================================================================
# MULTI-LAYER PERCEPTRON (MLP) BLOCKS
# =============================================================================
class Mlp(nn.Module):
"""MLP module used in Transformer blocks."""
def __init__(
self,
in_features: int,
hidden_features: Optional[int] = None,
out_features: Optional[int] = None,
act_layer: nn.Module = nn.GELU,
drop: float = 0.
):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
# =============================================================================
# WINDOW-BASED MULTI-HEAD SELF-ATTENTION WITH CLS TOKEN (CLS_WMSA)
# =============================================================================
class CLSWindowAttention(nn.Module):
"""
Window-based Multi-head Self-Attention with CLS token (CLS_WMSA).
This module implements the modified attention mechanism from the paper that
incorporates a class token into the Swin Transformer's window attention.
The CLS token communicates with all patch tokens across windows while
patch tokens only attend within their local windows.
Key equations from the paper:
- z^cls = Softmax(q0 · K^T / sqrt(d/H)) · V (Eq. 1)
- z_i = Softmax(q̄_i · k_i^T / sqrt(d/H)) · v_i (Eq. 3)
"""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
window_size: Tuple[int, int],
num_heads: int,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
attn_drop: float = 0.,
proj_drop: float = 0.
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # (Wh, Ww)
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
# Relative position bias table for window attention
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)
)
# Compute relative position index
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w], indexing='ij'))
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1)
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :]
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous()
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1)
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
# QKV projections
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, mask: Optional[Tensor] = None) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for CLS_WMSA.
Args:
x: Input tensor of shape (num_windows*B, N+1, C) where N = window_size^2
The first token is the CLS token
mask: Optional attention mask for shifted window attention
Returns:
Tuple of (output tensor, attention scores for CLS token)
"""
B_, N_plus_1, C = x.shape
N = N_plus_1 - 1 # Number of patch tokens (excluding CLS)
# Compute Q, K, V for all tokens
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N_plus_1, 3, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
qkv = qkv.permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4) # (3, B_, num_heads, N+1, head_dim)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
q = q * self.scale
# Separate CLS token and patch tokens
q_cls, q_patch = q[:, :, 0:1, :], q[:, :, 1:, :] # CLS: (B_, H, 1, d), patch: (B_, H, N, d)
k_cls, k_patch = k[:, :, 0:1, :], k[:, :, 1:, :]
v_cls, v_patch = v[:, :, 0:1, :], v[:, :, 1:, :]
# ============ CLS token attention (Eq. 1) ============
# CLS attends to all tokens (itself + all patches)
attn_cls = (q_cls @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # (B_, H, 1, N+1)
attn_cls = self.softmax(attn_cls)
attn_cls = self.attn_drop(attn_cls)
z_cls = (attn_cls @ v).squeeze(2) # (B_, H, d)
# ============ Patch token attention within windows (Eq. 3) ============
# Patches only attend to other patches within the same window
attn_patch = (q_patch @ k_patch.transpose(-2, -1)) # (B_, H, N, N)
# Add relative position bias
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[
self.relative_position_index.view(-1)
].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1
)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
attn_patch = attn_patch + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
# Apply mask for shifted window attention if provided
if mask is not None:
nW = mask.shape[0]
attn_patch = attn_patch.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn_patch = attn_patch + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn_patch = attn_patch.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn_patch = self.softmax(attn_patch)
attn_patch = self.attn_drop(attn_patch)
z_patch = (attn_patch @ v_patch) # (B_, H, N, d)
# Combine CLS and patch outputs
z_cls = z_cls.unsqueeze(2) # (B_, H, 1, d)
z = torch.cat([z_cls, z_patch], dim=2) # (B_, H, N+1, d)
z = z.transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N_plus_1, C)
# Output projection
z = self.proj(z)
z = self.proj_drop(z)
# Return attention scores for CLS token (used in LSM)
# Compute bidirectional attention score (Eq. 6-8)
attn_scores = attn_cls[:, :, 0, 1:] # CLS to patches: (B_, H, N)
return z, attn_scores
# =============================================================================
# SWIN TRANSFORMER BLOCK WITH CLS TOKEN
# =============================================================================
class CLSSwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
"""
Swin Transformer Block with CLS token support.
This block implements the modified Swin Transformer architecture that
incorporates a class token, enabling the computation of attention scores
between the CLS token and patch tokens for lesion selection.
"""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
num_heads: int,
window_size: int = 7,
shift_size: int = 0,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop: float = 0.,
attn_drop: float = 0.,
drop_path: float = 0.,
act_layer: nn.Module = nn.GELU,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = CLSWindowAttention(
dim, window_size=(window_size, window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop
)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim,
act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(
self,
x: Tensor,
cls_token: Tensor,
H: int,
W: int,
mask_matrix: Optional[Tensor] = None
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for the CLS Swin Transformer block.
Args:
x: Patch tokens of shape (B, H*W, C)
cls_token: CLS token of shape (B, 1, C)
H, W: Spatial dimensions
mask_matrix: Attention mask for shifted window attention
Returns:
Tuple of (updated patch tokens, updated CLS token, attention scores)
"""
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, f"Input feature has wrong size: {L} vs {H * W}"
shortcut_x = x
shortcut_cls = cls_token
# Normalize
x = self.norm1(x)
cls_token = self.norm1(cls_token)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# Pad feature maps to multiples of window size
pad_l = pad_t = 0
pad_r = (self.window_size - W % self.window_size) % self.window_size
pad_b = (self.window_size - H % self.window_size) % self.window_size
x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b))
_, Hp, Wp, _ = x.shape
# Cyclic shift for shifted window attention
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
attn_mask = mask_matrix
else:
shifted_x = x
attn_mask = None
# Partition into windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # (nW*B, ws, ws, C)
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C)
nW = x_windows.shape[0] // B
# Expand CLS token for each window
cls_token_expanded = cls_token.expand(-1, nW, -1).reshape(B * nW, 1, C)
# Concatenate CLS token with window tokens
x_windows_with_cls = torch.cat([cls_token_expanded, x_windows], dim=1)
# Apply attention
attn_output, attn_scores = self.attn(x_windows_with_cls, mask=attn_mask)
# Separate CLS and patch outputs
cls_out = attn_output[:, 0:1, :] # (B*nW, 1, C)
patch_out = attn_output[:, 1:, :] # (B*nW, ws*ws, C)
# Average CLS tokens across windows
cls_out = cls_out.view(B, nW, 1, C).mean(dim=1) # (B, 1, C)
# Average attention scores across windows for LSM
attn_scores = attn_scores.mean(dim=1) # Average over heads: (B*nW, N)
attn_scores = attn_scores.view(B, nW, -1) # (B, nW, ws*ws)
# Reshape patch tokens back to windows
patch_out = patch_out.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
# Reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = window_reverse(patch_out, self.window_size, Hp, Wp)
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = window_reverse(patch_out, self.window_size, Hp, Wp)
# Remove padding
if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0:
x = x[:, :H, :W, :].contiguous()
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
# Residual connection and MLP
x = shortcut_x + self.drop_path(x)
cls_token = shortcut_cls + self.drop_path(cls_out)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
cls_token = cls_token + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(cls_token)))
return x, cls_token, attn_scores
# =============================================================================
# PATCH EMBEDDING AND MERGING LAYERS
# =============================================================================
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""Image to Patch Embedding with CLS token."""
def __init__(
self,
img_size: int = 224,
patch_size: int = 4,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 96,
norm_layer: Optional[nn.Module] = None
):
super().__init__()
self.img_size = (img_size, img_size)
self.patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.patches_resolution = [img_size // patch_size, img_size // patch_size]
self.num_patches = self.patches_resolution[0] * self.patches_resolution[1]
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
# Learnable CLS token
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=.02)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, int, int]:
B, C, H, W = x.shape
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # (B, num_patches, embed_dim)
x = self.norm(x)
# Expand CLS token for batch
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(B, -1, -1)
Hp, Wp = H // self.patch_size[0], W // self.patch_size[1]
return x, cls_tokens, Hp, Wp
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
"""Patch Merging Layer for downsampling."""
def __init__(self, dim: int, norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)
self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim)
def forward(self, x: Tensor, H: int, W: int) -> Tuple[Tensor, int, int]:
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "Input feature has wrong size"
assert H % 2 == 0 and W % 2 == 0, f"x size ({H}*{W}) not even."
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# Merge 2x2 patches
x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :]
x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :]
x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :]
x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :]
x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1)
x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.reduction(x)
return x, H // 2, W // 2
# =============================================================================
# SWIN TRANSFORMER STAGE
# =============================================================================
class CLSSwinTransformerStage(nn.Module):
"""A single stage of the Swin Transformer with CLS token."""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
depth: int,
num_heads: int,
window_size: int,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop: float = 0.,
attn_drop: float = 0.,
drop_path: float = 0.,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm,
downsample: Optional[nn.Module] = None
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.depth = depth
self.window_size = window_size
# Build blocks with alternating shift sizes
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
CLSSwinTransformerBlock(
dim=dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer
)
for i in range(depth)
])
self.downsample = downsample
def create_mask(self, H: int, W: int, device: torch.device) -> Optional[Tensor]:
"""Create attention mask for shifted window attention."""
if self.window_size <= 0:
return None
Hp = int(math.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
Wp = int(math.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=device)
h_slices = (
slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -(self.window_size // 2)),
slice(-(self.window_size // 2), None)
)
w_slices = (
slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -(self.window_size // 2)),
slice(-(self.window_size // 2), None)
)
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size)
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0))
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
return attn_mask
def forward(self, x: Tensor, cls_token: Tensor, H: int, W: int) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, int, int]:
"""
Forward pass for the stage.
Returns:
Tuple of (patch tokens, CLS token, attention scores, H, W)
"""
attn_mask = self.create_mask(H, W, x.device)
all_attn_scores = []
for blk in self.blocks:
x, cls_token, attn_scores = blk(x, cls_token, H, W, attn_mask)
all_attn_scores.append(attn_scores)
if self.downsample is not None:
x, H, W = self.downsample(x, H, W)
# Use attention scores from last block
final_attn_scores = all_attn_scores[-1]
return x, cls_token, final_attn_scores, H, W
# =============================================================================
# GLOBAL FEATURE ENCODER (Gθ)
# =============================================================================
class GlobalFeatureEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
Global Feature Encoder (Gθ) based on Swin Transformer.
This encoder processes downsampled clinical images to extract global
contextual features and compute attention scores for lesion selection.
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_size: int = 384,
patch_size: int = 4,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 96,
depths: List[int] = [2, 2, 6, 2],
num_heads: List[int] = [3, 6, 12, 24],
window_size: int = 7,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm
):
super().__init__()
self.num_stages = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_stages - 1))
# Patch embedding
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim, norm_layer=norm_layer
)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# Stochastic depth decay rule
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
# Build stages
self.stages = nn.ModuleList()
for i_stage in range(self.num_stages):
stage = CLSSwinTransformerStage(
dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage),
depth=depths[i_stage],
num_heads=num_heads[i_stage],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_stage]):sum(depths[:i_stage + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging(int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage), norm_layer)
if i_stage < self.num_stages - 1 else None
)
self.stages.append(stage)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
# CLS token projection for matching dimensions across stages
self.cls_projections = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Linear(embed_dim, int(embed_dim * 2 ** i)) if i > 0 else nn.Identity()
for i in range(self.num_stages)
])
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Global Feature Encoder.
Args:
x: Input image tensor of shape (B, C, H, W)
Returns:
Tuple of (global CLS feature, patch features, attention scores for LSM)
"""
# Patch embedding
x, cls_token, H, W = self.patch_embed(x)
x = self.pos_drop(x)
# Process through stages
for i, stage in enumerate(self.stages):
# Project CLS token to match stage dimension
if i > 0:
cls_token = self.cls_projections[i](cls_token)
x, cls_token, attn_scores, H, W = stage(x, cls_token, H, W)
# Normalize
x = self.norm(x)
cls_token = self.norm(cls_token)
return cls_token.squeeze(1), x, attn_scores
# =============================================================================
# LESION SELECTION MODULE (LSM)
# =============================================================================
class LesionSelectionModule(nn.Module):
"""
Lesion Selection Module (LSM) for extracting high-resolution lesion patches.
This module uses attention scores from the global encoder to identify
regions most likely to contain lesions, then extracts corresponding
patches from the original high-resolution image.
Key features:
- Uses bidirectional attention scores (Eq. 6-8)
- Implements attention sampling for differentiable selection
- Selects top-K patches with highest attention scores
"""
def __init__(
self,
num_patches: int = 4,
patch_size: int = 224,
feature_map_size: int = 12,
window_size: int = 7,
use_attention_sampling: bool = True,
sampling_n: int = 10
):
super().__init__()
self.num_patches = num_patches # Kp in the paper
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.feature_map_size = feature_map_size
self.window_size = window_size
self.use_attention_sampling = use_attention_sampling
self.sampling_n = sampling_n
def compute_attention_scores(self, attn_scores: Tensor, H: int, W: int) -> Tensor:
"""
Compute global attention scores from window-based attention.
Args:
attn_scores: Attention scores from global encoder (B, nW, ws*ws)
H, W: Feature map spatial dimensions
Returns:
Global attention map of shape (B, H, W)
"""
B = attn_scores.shape[0]
nW_h = H // self.window_size
nW_w = W // self.window_size
# Reshape to spatial layout
attn_map = attn_scores.view(B, nW_h, nW_w, self.window_size, self.window_size)
attn_map = attn_map.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4).contiguous()
attn_map = attn_map.view(B, H, W)
return attn_map
def select_patches_topk(
self,
x_hr: Tensor,
attn_map: Tensor
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Select top-K patches based on attention scores.
Args:
x_hr: High-resolution input image (B, C, H_hr, W_hr)
attn_map: Attention map (B, H_feat, W_feat)
Returns:
Tuple of (selected patches, patch indices)
"""
B, C, H_hr, W_hr = x_hr.shape
H_feat, W_feat = attn_map.shape[1], attn_map.shape[2]
# Compute scale factor between feature map and high-res image
scale_h = H_hr / H_feat
scale_w = W_hr / W_feat
# Flatten attention map and get top-K indices
attn_flat = attn_map.view(B, -1) # (B, H_feat * W_feat)
_, topk_indices = torch.topk(attn_flat, self.num_patches, dim=1)
# Convert flat indices to 2D coordinates
topk_h = topk_indices // W_feat
topk_w = topk_indices % W_feat
# Extract patches from high-resolution image
patches = []
half_patch = self.patch_size // 2
for b in range(B):
batch_patches = []
for k in range(self.num_patches):
# Center coordinates in high-res image
center_h = int((topk_h[b, k].float() + 0.5) * scale_h)
center_w = int((topk_w[b, k].float() + 0.5) * scale_w)
# Compute patch boundaries with clamping
top = max(0, center_h - half_patch)
left = max(0, center_w - half_patch)
bottom = min(H_hr, top + self.patch_size)
right = min(W_hr, left + self.patch_size)
# Adjust if patch extends beyond image
if bottom - top < self.patch_size:
top = max(0, bottom - self.patch_size)
if right - left < self.patch_size:
left = max(0, right - self.patch_size)
patch = x_hr[b:b+1, :, top:bottom, left:right]
# Resize if necessary
if patch.shape[2] != self.patch_size or patch.shape[3] != self.patch_size:
patch = F.interpolate(patch, size=(self.patch_size, self.patch_size),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
batch_patches.append(patch)
patches.append(torch.cat(batch_patches, dim=0))
patches = torch.stack(patches, dim=0) # (B, Kp, C, patch_size, patch_size)
return patches, topk_indices
def attention_sampling(
self,
x_hr: Tensor,
attn_map: Tensor
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Differentiable attention sampling for patch selection (Eq. 9).
This implements the Monte Carlo approximation described in the paper
to make the lesion selection differentiable.
"""
B, C, H_hr, W_hr = x_hr.shape
H_feat, W_feat = attn_map.shape[1], attn_map.shape[2]
# Normalize attention map to probability distribution
attn_flat = attn_map.view(B, -1)
attn_probs = F.softmax(attn_flat, dim=1)
# Sample indices according to attention distribution
sampled_indices = torch.multinomial(attn_probs, self.sampling_n, replacement=True)
# Use top-K from sampled indices based on their attention scores
sampled_attn = torch.gather(attn_flat, 1, sampled_indices)
_, topk_in_sample = torch.topk(sampled_attn, self.num_patches, dim=1)
topk_indices = torch.gather(sampled_indices, 1, topk_in_sample)
# Extract patches using the sampled indices
return self._extract_patches_from_indices(x_hr, topk_indices, H_feat, W_feat)
def _extract_patches_from_indices(
self,
x_hr: Tensor,
indices: Tensor,
H_feat: int,
W_feat: int
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""Helper to extract patches given flat indices."""
B, C, H_hr, W_hr = x_hr.shape
scale_h = H_hr / H_feat
scale_w = W_hr / W_feat
topk_h = indices // W_feat
topk_w = indices % W_feat
patches = []
half_patch = self.patch_size // 2
for b in range(B):
batch_patches = []
for k in range(self.num_patches):
center_h = int((topk_h[b, k].float() + 0.5) * scale_h)
center_w = int((topk_w[b, k].float() + 0.5) * scale_w)
top = max(0, center_h - half_patch)
left = max(0, center_w - half_patch)
bottom = min(H_hr, top + self.patch_size)
right = min(W_hr, left + self.patch_size)
if bottom - top < self.patch_size:
top = max(0, bottom - self.patch_size)
if right - left < self.patch_size:
left = max(0, right - self.patch_size)
patch = x_hr[b:b+1, :, top:bottom, left:right]
if patch.shape[2] != self.patch_size or patch.shape[3] != self.patch_size:
patch = F.interpolate(patch, size=(self.patch_size, self.patch_size),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
batch_patches.append(patch)
patches.append(torch.cat(batch_patches, dim=0))
patches = torch.stack(patches, dim=0)
return patches, indices
def forward(
self,
x_hr: Tensor,
attn_scores: Tensor,
H: int,
W: int
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Lesion Selection Module.
Args:
x_hr: High-resolution input image (B, C, H_hr, W_hr)
attn_scores: Attention scores from global encoder
H, W: Feature map spatial dimensions
Returns:
Tuple of (selected patches, attention map)
"""
# Compute spatial attention map
attn_map = self.compute_attention_scores(attn_scores, H, W)
# Select patches
if self.training and self.use_attention_sampling:
patches, indices = self.attention_sampling(x_hr, attn_map)
else:
patches, indices = self.select_patches_topk(x_hr, attn_map)
return patches, attn_map
# =============================================================================
# LOCAL FEATURE ENCODER (Lθ)
# =============================================================================
class LocalFeatureEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
Local Feature Encoder (Lθ) for processing selected lesion patches.
This encoder shares the first three stages with the global encoder
but has an independent final stage to capture fine-grained lesion details.
"""
def __init__(
self,
patch_size: int = 4,
in_chans: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 96,
depths: List[int] = [2, 2, 6, 2],
num_heads: List[int] = [3, 6, 12, 24],
window_size: int = 7,
mlp_ratio: float = 4.,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
drop_rate: float = 0.,
attn_drop_rate: float = 0.,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.1,
norm_layer: nn.Module = nn.LayerNorm,
shared_stages: Optional[nn.ModuleList] = None
):
super().__init__()
self.num_stages = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_stages - 1))
# Patch embedding (can be shared or independent)
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=224, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim, norm_layer=norm_layer
)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# Stochastic depth
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
# Build stages - first 3 shared, last 1 independent
if shared_stages is not None:
self.stages = nn.ModuleList(list(shared_stages[:3]))
else:
self.stages = nn.ModuleList()
for i_stage in range(self.num_stages - 1):
stage = CLSSwinTransformerStage(
dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage),
depth=depths[i_stage],
num_heads=num_heads[i_stage],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_stage]):sum(depths[:i_stage + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging(int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage), norm_layer)
)
self.stages.append(stage)
# Independent final stage
i_stage = self.num_stages - 1
self.final_stage = CLSSwinTransformerStage(
dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage),
depth=depths[i_stage],
num_heads=num_heads[i_stage],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_stage]):sum(depths[:i_stage + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=None
)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
# CLS token projections
self.cls_projections = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Linear(embed_dim, int(embed_dim * 2 ** i)) if i > 0 else nn.Identity()
for i in range(self.num_stages)
])
def forward(self, patches: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Local Feature Encoder.
Args:
patches: Selected lesion patches (B, Kp, C, H, W)
Returns:
Tuple of (CLS features, patch features) for all Kp patches
"""
B, Kp, C, H, W = patches.shape
# Process each patch
cls_features = []
patch_features = []
for k in range(Kp):
patch = patches[:, k] # (B, C, H, W)
# Patch embedding
x, cls_token, Hp, Wp = self.patch_embed(patch)
x = self.pos_drop(x)
# Process through shared stages
for i, stage in enumerate(self.stages):
if i > 0:
cls_token = self.cls_projections[i](cls_token)
x, cls_token, _, Hp, Wp = stage(x, cls_token, Hp, Wp)
# Project CLS for final stage
cls_token = self.cls_projections[-1](cls_token)
# Process through final stage
x, cls_token, _, Hp, Wp = self.final_stage(x, cls_token, Hp, Wp)
# Normalize
x = self.norm(x)
cls_token = self.norm(cls_token)
cls_features.append(cls_token.squeeze(1))
patch_features.append(x)
# Stack features from all patches
cls_features = torch.stack(cls_features, dim=1) # (B, Kp, dim)
patch_features = torch.stack(patch_features, dim=1) # (B, Kp, N, dim)
return cls_features, patch_features
# =============================================================================
# CROSS-SCALE FUSION MODULE (CSF)
# =============================================================================
class CrossScaleFusion(nn.Module):
"""
Cross-Scale Fusion (CSF) Module for combining global and local features.
This module implements the feature alignment and fusion mechanism
described in Equations 10-14 of the paper, using cross-attention
to exchange information between global and local representations.
"""
def __init__(
self,
dim: int,
num_heads: int = 8,
qkv_bias: bool = True,
attn_drop: float = 0.,
proj_drop: float = 0.
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
# Projections for global-to-local attention (Eq. 10)
self.W_Q_lg = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_K_lg = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_V_lg = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
# Projections for local-to-global attention (Eq. 11)
self.W_Q_gl = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_K_gl = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_V_gl = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
# Output projections
self.proj_g = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_l = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
# Layer normalization
self.norm_g = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.norm_l = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
def forward(
self,
g_cls: Tensor,
g_patch: Tensor,
l_cls: Tensor,
l_patch: Tensor
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass for Cross-Scale Fusion.
Args:
g_cls: Global CLS feature (B, dim)
g_patch: Global patch features (B, N_g, dim)
l_cls: Local CLS features (B, Kp, dim)
l_patch: Local patch features (B, Kp, N_l, dim)
Returns:
Tuple of (fused global feature, fused local features)
"""
B = g_cls.shape[0]
Kp = l_cls.shape[1]
# Reshape local features
l_cls_flat = l_cls.view(B, Kp, -1) # (B, Kp, dim)
l_patch_flat = l_patch.view(B, -1, self.dim) # (B, Kp*N_l, dim)
# ============ Construct new feature tensors (Fig. 5) ============
# g̃ = [g_cls, g_patch]; l̂ = [l_cls, l_patch]
g_tilde = torch.cat([g_cls.unsqueeze(1), g_patch], dim=1) # (B, 1+N_g, dim)
l_hat = torch.cat([l_cls_flat, l_patch_flat], dim=1) # (B, Kp+Kp*N_l, dim)
# ĝ = [l_cls, g_patch]; l̃ = [g_cls, l_patch]
g_hat = torch.cat([l_cls_flat, g_patch], dim=1) # (B, Kp+N_g, dim)
l_tilde = torch.cat([g_cls.unsqueeze(1), l_patch_flat], dim=1) # (B, 1+Kp*N_l, dim)
# Normalize
g_tilde = self.norm_g(g_tilde)
l_hat = self.norm_l(l_hat)
g_hat = self.norm_g(g_hat)
l_tilde = self.norm_l(l_tilde)
# ============ Global feature update (Eq. 10, 12) ============
Q_g = self.W_Q_lg(g_tilde)
K_g = self.W_K_lg(l_hat)
V_g = self.W_V_lg(l_hat)
# Reshape for multi-head attention
Q_g = Q_g.view(B, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
K_g = K_g.view(B, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
V_g = V_g.view(B, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
attn_g = (Q_g @ K_g.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn_g = F.softmax(attn_g, dim=-1)
attn_g = self.attn_drop(attn_g)
M_g_cross = (attn_g @ V_g).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, -1, self.dim)
M_g_cross = self.proj_g(M_g_cross)
M_g_cross = self.proj_drop(M_g_cross)
# ============ Local feature update (Eq. 11, 13) ============
Q_l = self.W_Q_gl(l_tilde)
K_l = self.W_K_gl(g_hat)
V_l = self.W_V_gl(g_hat)
Q_l = Q_l.view(B, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
K_l = K_l.view(B, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
V_l = V_l.view(B, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
attn_l = (Q_l @ K_l.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn_l = F.softmax(attn_l, dim=-1)
attn_l = self.attn_drop(attn_l)
M_l_cross = (attn_l @ V_l).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, -1, self.dim)
M_l_cross = self.proj_l(M_l_cross)
M_l_cross = self.proj_drop(M_l_cross)
# ============ Residual connections (Eq. 14) ============
g_C = g_tilde + M_g_cross
l_C = l_tilde + M_l_cross
# Extract final features
g_out = g_C[:, 0] # Global CLS feature (B, dim)
l_out = l_C[:, 0] # Use first token as local representative (B, dim)
return g_out, l_outReferences
Related posts, You May like to read
- 7 Shocking Truths About Knowledge Distillation: The Good, The Bad, and The Breakthrough (SAKD)
- 7 Revolutionary Breakthroughs in Medical Image Translation (And 1 Fatal Flaw That Could Derail Your AI Model)
- TimeDistill: Revolutionizing Time Series Forecasting with Cross-Architecture Knowledge Distillation
- HiPerformer: A New Benchmark in Medical Image Segmentation with Modular Hierarchical Fusion
- GeoSAM2 3D Part Segmentation — Prompt-Controllable, Geometry-Aware Masks for Precision 3D Editing
- DGRM: How Advanced AI is Learning to Detect Machine-Generated Text Across Different Domains
- A Knowledge Distillation-Based Approach to Enhance Transparency of Classifier Models
- Towards Trustworthy Breast Tumor Segmentation in Ultrasound Using AI Uncertainty
- Discrete Migratory Bird Optimizer with Deep Transfer Learning for Multi-Retinal Disease Detection