Introduction
Video segmentation has become increasingly critical in computer vision applications, from autonomous driving to video editing and surveillance systems. However, existing approaches struggle with a fundamental challenge: how to accurately track and segment objects across long, complex videos while simultaneously identifying both foreground “things” (like people and cars) and background “stuff” (like roads and sky). Enter DVIS++, an innovative decoupled framework that fundamentally reimagines how machines understand video content. Rather than attempting to model video segmentation in one end-to-end process, DVIS++ breaks the problem into three manageable sub-tasks: segmentation, tracking, and refinement. This breakthrough approach has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance across six major benchmarks, achieving an impressive 68.3 AP on YouTube-VIS 2019 and outperforming previous SOTA methods by significant margins. This article explores how DVIS++ works, why its decoupled design matters, and what its achievements mean for the future of video understanding AI.
Understanding Video Segmentation: Why Current Methods Fall Short
Before exploring DVIS++, it’s essential to understand why video segmentation remains such a challenging problem. Traditional approaches typically fall into two categories:
Offline Methods attempt to process entire videos at once, extracting spatio-temporal features to identify and track objects. While effective on short, simple videos, these methods struggle dramatically with complex, lengthy videos featuring severe occlusions, rapid movements, and deformations. The computational complexity of linking identical objects across hundreds of frames becomes prohibitive.
Online Methods take a frame-by-frame approach, associating objects between consecutive frames. They perform better on longer videos but fail to effectively model the long-term spatio-temporal relationships essential for robust segmentation. This creates a critical gap: neither approach optimally balances temporal efficiency with long-term consistency.
DVIS++ solves this fundamental tension through strategic decoupling, enabling researchers to achieve superior performance across both simple and complex scenarios.
The Decoupled Design: Breaking Down Complexity
How DVIS++ Structures the Problem
The revolutionary insight behind DVIS++ lies in its decoupled architecture, which divides universal video segmentation into three independent, sequential sub-tasks:
$$ \small \renewcommand{\arraystretch}{1.25} \begin{array}{l|l|l} \hline \textbf{Component} & \textbf{Function} & \textbf{Complexity} \\ \hline \text{Segmenter} & \text{Extracts object representations from individual frames} & \text{Independent of video length} \\ \text{Referring Tracker} & \text{Establishes frame-by-frame object associations} & \text{Reduced to adjacent frames only} \\ \text{Temporal Refiner} & \text{Models spatio-temporal relationships from aligned representations} & \text{Simplified by pre-aligned features} \\ \hline \end{array} $$This decomposition is conceptually elegant yet practically powerful. By pre-aligning object representations across frames, subsequent components work with significantly cleaner inputs, reducing compounding errors and computational demands.
Mathematical Foundation:
The framework processes video through:
\[ Q_{Seg}, S, M = \text{Segmenter}(I) \]where QSeg ∈ RN x C represents object representations, S contains confidence scores, and M represents segmentation masks for image I.
The referring tracker then operates:
\[ Q^T_{RT}, \text{Ref}^T = \mathcal{T}(\text{Ref}^{T-1}, Q^T_{Seg}, \text{Noiser}(Q^T_{Seg})) \]This design reduces tracking complexity from “link all frames” to “link adjacent frames,” a transformative simplification that enables effective long-term modeling.
Key Innovations: The Referring Tracker and Temporal Refiner
The Referring Tracker: Intelligent Object Association
The referring tracker represents DVIS++’s most novel contribution. Rather than employing heuristic matching algorithms, it models tracking as a denoising task. During training, the framework intentionally corrupts object representations using three sophisticated noise simulation strategies:
- Random Weighted Averaging – Blending representations from different objects to simulate occlusion and confusion
- Random Cropping & Concatenation – Fragmenting features to simulate partial visibility
- Random Shuffling – Randomizing object order to force robust association learning
This counterintuitive training approach forces the tracker to develop genuine discriminative capabilities rather than relying on identity shortcuts. Ablation studies confirm this denoising strategy alone contributes +3.7 AP, with particularly strong gains on occluded objects (+4.1 AP for heavy occlusion).
The tracker employs Referring Cross-Attention (RCA), a specialized attention mechanism that leverages the similarity between corresponding objects across frames:
\[ \text{RCA}(\text{ID}, Q, K, V) = \text{ID} + \text{MHA}(Q, K, V) \]where ID represents noisy initial values, Q provides reference information, and K&V supply object features.
The Temporal Refiner: Comprehensive Spatio-Temporal Modeling
Once objects are properly aligned across frames, the temporal refiner extracts both short-term and long-term temporal relationships through an elegant two-stream approach:
- Short-term modeling uses 1D convolution to capture immediate frame-to-frame changes
- Long-term modeling employs multi-head self-attention to identify patterns across the entire video sequence
This design respects the different temporal scales at which meaningful patterns emerge. Ablation studies reveal:
- Removing long-term attention causes -3.2 AP performance loss
- Removing short-term convolution results in -0.2 AP degradation
- Both components prove essential for comprehensive understanding
Advancing Through Contrastive Learning
Beyond the core architecture, DVIS++ incorporates contrastive learning across all three components to produce more discriminative object representations. The framework maintains separate contrastive item construction for each module:
For the Segmenter: Each object representation anchors against representations from the same frame (negatives) and the same object across frames (positives), incorporating momentum-averaged features for temporal consistency.
For the Referring Tracker: References from adjacent frames serve as positives, while references from the same frame serve as negatives, enforcing frame-to-frame consistency.
For the Temporal Refiner: A fixed-length memory bank stores representations from previous batches, enabling sophisticated hard negative mining to suppress identity swapping.
Performance gains from contrastive learning are substantial: +0.8 AP for the segmenter, +0.7 AP for the tracker, and particularly significant improvements on lightly occluded objects (+8.0 AP).
Vision Foundation Models: Enabling Flexible Deployment
DINOv2 Integration for Frozen Backbone Training
DVIS++ integrates DINOv2, a self-supervised vision foundation model, enabling the framework to operate with a completely frozen backbone. Using VIT-Adapter to generate multi-scale features from the ViT backbone, the system achieves remarkable performance without any fine-tuning, demonstrating the generalizability of the decoupled approach.
Open-Vocabulary Capabilities: OV-DVIS++
By integrating CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training), the framework enables zero-shot video segmentation on arbitrary categories. OV-DVIS++ achieves:
- 34.5 AP on YouTube-VIS 2019 (ResNet-50)
- 48.8 AP on YouTube-VIS 2019 (ConvNext-L)
- 11.4 AP improvement over previous SOTA methods
Remarkably, this performance emerges from training exclusively on COCO, without exposure to video-specific data, showcasing extraordinary generalization capability.
Benchmark Performance: Comprehensive Validation Across Domains
DVIS++ demonstrates superior performance across six major benchmarks:
Video Instance Segmentation (VIS)
$$ \small \renewcommand{\arraystretch}{1.25} \begin{array}{l|c|c|c|c} \hline \textbf{Dataset} & \textbf{Metric} & \textbf{DIVS++} & \textbf{Previous SOTA} & \textbf{Improvement} \\ \hline \text{YouTube-VIS 2019} & \text{AP (VIT-L, offline)} & 68.3 & 66.9 & +1.4 \\ \text{YouTube-VIS 2021} & \text{AP (VIT-L, offline)} & 63.9 & 61.2 & +2.7 \\ \text{OVIS} & \text{AP (VIT-L, offline)} & 53.4 & 45.4 & +8.0 \\ \text{YouTube-VIS 2022} & \text{APL (VIT-L, offline)} & 50.9 & 44.3 & +6.6 \\ \hline \end{array} $$The 8.0 AP improvement on OVIS, which features exceptionally long videos with severe occlusion, validates DVIS++’s effectiveness on real-world challenging scenarios.
Video Semantic Segmentation (VSS) and Panoptic Segmentation (VPS)
On VSPW (semantic segmentation), DVIS++ achieves 95.7% mVC8 and 63.8% mIoU, surpassing all competitors. On VIPSeg (panoptic segmentation), the framework achieves 58.0 VPQ in offline mode, outperforming the previous SOTA TarVIS by 10.0 VPQ.
Technical Excellence: Ablation Study Insights
Comprehensive ablation studies illuminate how each component contributes to overall performance:
- Referring tracker alone: +7.0 AP (demonstrating the power of learnable tracking)
- Temporal refiner: +4.0 AP additional gain
- Denoising strategy: +3.7 AP improvement
- Contrastive learning: Variable impact depending on occlusion level
These ablations confirm that architectural choices weren’t arbitrary but rather carefully optimized based on empirical evidence.
Practical Applications and Real-World Impact
DVIS++ enables numerous practical applications previously limited by segmentation accuracy constraints:
- Autonomous Driving: Precise understanding of dynamic obstacles, pedestrians, and road boundaries across extended video sequences.
- Video Editing: Intelligent object isolation and manipulation in complex scenes with multiple occluding elements.
- Surveillance and Security: Robust tracking and classification of persons and objects under challenging conditions.
- Medical Imaging: Temporal consistency in video-based medical procedures and anatomical tracking.
The framework’s ability to handle both “thing” and “stuff” categories simultaneously distinguishes it from specialized methods, making DVIS++ genuinely universal.
Looking Forward: Future Implications
While DVIS++ represents a significant advance, acknowledged limitations suggest promising future directions:
- Fast-moving objects occasionally cause false identity associations when motion exceeds the tracker’s temporal window
- Segmenter limitations propagate through the pipeline; improving base segmentation would proportionally enhance tracking and refinement
These challenges present opportunities for continued innovation in motion modeling and robust feature extraction.
Conclusion: A Paradigm Shift in Video Understanding
DVIS++ fundamentally reimagines video segmentation through strategic decoupling, transforming what was once an intractable end-to-end problem into three manageable, well-designed sub-tasks. By introducing the referring tracker’s denoising-based approach, incorporating sophisticated contrastive learning, and demonstrating effectiveness with foundation models, the framework achieves unprecedented performance across diverse benchmarks while maintaining practical applicability.
The consistent improvements—particularly the 8.0 AP gain on OVIS for complex real-world scenarios—validate that the decoupled design philosophy offers genuine advances, not merely incremental optimization of existing approaches.
Ready to Explore Advanced Video AI?
The evolution of video segmentation technology directly impacts numerous fields, from robotics to creative applications. Whether you’re developing computer vision systems, researching AI architectures, or implementing video understanding solutions, understanding frameworks like DVIS++ provides essential context for making informed technical decisions.
What aspects of video segmentation matter most to your work? Explore implementation details in the official DVIS++ GitHub repository, experiment with pre-trained models, or engage with the research community to contribute to the next generation of video understanding technology. For more information, please download the full paper and read it here.
Share your insights, questions, or applications in the comments below—let’s advance the field together.
Here is the comprehensive, production-ready implementation of DVIS++ in PyTorch. This implementation includes all core components: Segmenter, Referring Tracker, Temporal Refiner, and training/inference pipelines.
"""
Utility functions and helper modules for DVIS++
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Optional
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
class NestedTensor:
"""Helper class for handling nested tensors with masks"""
def __init__(self, tensors, mask):
self.tensors = tensors
self.mask = mask
def to(self, device):
cast_tensor = self.tensors.to(device)
mask = self.mask
if mask is not None:
cast_mask = mask.to(device)
else:
cast_mask = None
return NestedTensor(cast_tensor, cast_mask)
@property
def device(self):
return self.tensors.device
def get_clones(module, N):
"""Clone a module N times"""
return nn.ModuleList([__import__('copy').deepcopy(module) for i in range(N)])
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
"""Standard Multi-Head Attention mechanism"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, attn_drop=0.0, proj_drop=0.0):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
self.to_qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
"""Position-wise Feed-Forward Network"""
def __init__(self, dim, hidden_dim, dropout=0.0):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim),
nn.Dropout(dropout)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
class HungarianMatcher(nn.Module):
"""Hungarian algorithm for bipartite matching"""
def __init__(self, cost_class=1, cost_mask=1, cost_dice=1):
super().__init__()
self.cost_class = cost_class
self.cost_mask = cost_mask
self.cost_dice = cost_dice
@torch.no_grad()
def forward(self, outputs, targets):
"""
Performs the matching
Args:
outputs: This is a dict that contains at least these entries:
"pred_logits": Tensor of dim [batch_size, num_queries, num_classes]
"pred_masks": Tensor of dim [batch_size, num_queries, H, W]
targets: This is a list of targets (len = batch_size), where each target is a dict
containing:
"labels": Tensor of dim [num_target_boxes]
"masks": Tensor of dim [num_target_boxes, H, W]
"""
bs, num_queries = outputs["pred_logits"].shape[:2]
# We flatten to compute the cost matrices in a batch
out_prob = outputs["pred_logits"].flatten(0, 1).softmax(-1)
out_mask = outputs["pred_masks"].flatten(0, 1)
tgt_ids = torch.cat([v["labels"] for v in targets])
tgt_mask = torch.cat([v["masks"] for v in targets])
cost_class = -out_prob[:, tgt_ids]
# Compute the dice loss
cost_dice = self.dice_loss(out_mask, tgt_mask)
# Compute the mask loss
cost_mask = self.mask_loss(out_mask, tgt_mask)
C = (self.cost_class * cost_class +
self.cost_dice * cost_dice +
self.cost_mask * cost_mask)
C = C.cpu()
sizes = [len(v["masks"]) for v in targets]
indices = [linear_sum_assignment(c[i]) for i, c in enumerate(C.split(sizes))]
return [(torch.as_tensor(i, dtype=torch.int64),
torch.as_tensor(j, dtype=torch.int64)) for i, j in indices]
@staticmethod
def dice_loss(inputs, targets):
"""Compute the DICE loss"""
inputs = inputs.sigmoid()
numerator = 2 * (inputs * targets).sum(-1)
denominator = inputs.sum(-1) + targets.sum(-1)
loss = 1 - (numerator + 1) / (denominator + 1)
return loss
@staticmethod
def mask_loss(inputs, targets):
"""Compute the Mask (cross-entropy) loss"""
inputs = inputs.sigmoid()
return F.binary_cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='none').mean(-1)
class MemoryBank(nn.Module):
"""Fixed-size memory bank for storing embeddings"""
def __init__(self, capacity=4096, dim=256):
super().__init__()
self.capacity = capacity
self.dim = dim
self.register_buffer('bank', torch.randn(capacity, dim))
self.register_buffer('pointer', torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.long))
def update(self, x):
"""Push new embeddings to the bank"""
batch_size = x.shape[0]
ptr = int(self.pointer)
if ptr + batch_size <= self.capacity:
self.bank[ptr:ptr + batch_size] = x.detach()
else:
remaining = self.capacity - ptr
self.bank[ptr:] = x[:remaining].detach()
self.bank[:batch_size - remaining] = x[remaining:].detach()
self.pointer[0] = (ptr + batch_size) % self.capacity
def get(self):
"""Get all stored embeddings"""
return self.bank
class NoiseSimulator(nn.Module):
"""Generates noise for denoising training strategy"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x, strategy='weighted_avg', prob=0.5):
"""
Simulate noise in object representations
Args:
x: Tensor of shape [N, C]
strategy: One of 'weighted_avg', 'crop_concat', 'shuffle'
prob: Probability of applying noise
Returns:
Noised tensor of shape [N, C]
"""
if not self.training or torch.rand(1).item() > prob:
return x
N, C = x.shape
if strategy == 'weighted_avg':
return self._weighted_avg_noise(x)
elif strategy == 'crop_concat':
return self._crop_concat_noise(x)
elif strategy == 'shuffle':
return self._shuffle_noise(x)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown strategy: {strategy}")
@staticmethod
def _weighted_avg_noise(x):
"""Random weighted averaging"""
N, C = x.shape
noised = x.clone()
for i in range(N):
j = torch.randint(0, N, (1,)).item()
alpha = torch.rand(1).item()
noised[i] = alpha * x[i] + (1 - alpha) * x[j]
return noised
@staticmethod
def _crop_concat_noise(x):
"""Random cropping and concatenation"""
N, C = x.shape
noised = x.clone()
for i in range(N):
j = torch.randint(0, N, (1,)).item()
k = torch.randint(0, C, (1,)).item()
noised[i, :k] = x[i, :k]
noised[i, k:] = x[j, k:]
return noised
@staticmethod
def _shuffle_noise(x):
"""Random shuffling"""
indices = torch.randperm(x.shape[0])
return x[indices]
class ContrastiveLoss(nn.Module):
"""InfoNCE-based contrastive loss"""
def __init__(self, temperature=0.07):
super().__init__()
self.temperature = temperature
def forward(self, anchor, positives, negatives):
"""
Compute contrastive loss
Args:
anchor: Anchor embedding [B, D]
positives: Positive embeddings [B, K_pos, D]
negatives: Negative embeddings [B, K_neg, D]
Returns:
Scalar loss
"""
B, D = anchor.shape
# Normalize
anchor = F.normalize(anchor, dim=-1)
positives = F.normalize(positives, dim=-1)
negatives = F.normalize(negatives, dim=-1)
# Compute similarities
pos_sim = (anchor.unsqueeze(1) * positives).sum(-1) / self.temperature # [B, K_pos]
neg_sim = (anchor.unsqueeze(1) * negatives).sum(-1) / self.temperature # [B, K_neg]
# Compute loss
loss = -torch.log(
torch.exp(pos_sim.logsumexp(dim=1)) /
(torch.exp(pos_sim.logsumexp(dim=1)) + torch.exp(neg_sim.logsumexp(dim=1)))
)
return loss.mean()
def compute_dice_loss(inputs, targets):
"""Compute DICE loss"""
smooth = 1.0
intersection = (inputs * targets).sum()
union = inputs.sum() + targets.sum()
dice = (2.0 * intersection + smooth) / (union + smooth)
return 1.0 - dice
def compute_sigmoid_focal_loss(inputs, targets, alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0):
"""Compute Focal loss"""
p = torch.sigmoid(inputs)
ce_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(inputs, targets, reduction='none')
p_t = p * targets + (1 - p) * (1 - targets)
loss = ce_loss * ((1 - p_t) ** gamma)
if alpha >= 0:
alpha_t = alpha * targets + (1 - alpha) * (1 - targets)
loss = alpha_t * loss
return loss.mean()
class TemporalWeighting(nn.Module):
"""Compute temporal weights for category representation"""
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
"""
Compute weighted aggregation across temporal dimension
Args:
x: Tensor of shape [N, T, C]
Returns:
Weighted representation of shape [N, C]
"""
N, T, C = x.shape
# Compute weights
weights = self.linear(x).squeeze(-1) # [N, T]
weights = F.softmax(weights, dim=1) # [N, T]
# Aggregate
output = (x * weights.unsqueeze(-1)).sum(dim=1) # [N, C]
return output"""
Training utilities and data loading for DVIS++
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import torchvision.transforms as T
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class VideoSegmentationDataset(Dataset):
"""Generic video segmentation dataset"""
def __init__(
self,
video_dir: str,
anno_file: str,
num_frames: int = 5,
image_size: Tuple[int, int] = (512, 512),
split: str = 'train'
):
self.video_dir = Path(video_dir)
self.num_frames = num_frames
self.image_size = image_size
self.split = split
# Load annotations
with open(anno_file, 'r') as f:
self.annotations = json.load(f)
# Image transforms
self.transforms = T.Compose([
T.Resize(image_size),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
def __len__(self):
return len(self.annotations)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
video_info = self.annotations[idx]
video_name = video_info['video_id']
frames_info = video_info['frames']
# Sample frames
num_available = len(frames_info)
if num_available >= self.num_frames:
# Uniformly sample frames
indices = np.linspace(0, num_available - 1,
self.num_frames, dtype=int)
else:
# Repeat frames if not enough
indices = np.arange(num_available)
while len(indices) < self.num_frames:
indices = np.concatenate([
indices,
np.random.choice(np.arange(num_available),
self.num_frames - len(indices))
])
# Load frames and annotations
frames = []
targets = []
for frame_idx in indices:
frame_info = frames_info[frame_idx]
frame_path = self.video_dir / video_name / f"{frame_idx:06d}.jpg"
# Load image
from PIL import Image
img = Image.open(frame_path).convert('RGB')
img_tensor = self.transforms(img)
frames.append(img_tensor)
# Load segmentation masks and labels
masks = []
labels = []
for obj_id, obj_info in frame_info.get('objects', {}).items():
mask_path = (self.video_dir / video_name /
f"mask_{frame_idx:06d}_{obj_id}.png")
if mask_path.exists():
mask = Image.open(mask_path).convert('L')
mask = T.Resize(self.image_size)(mask)
mask_tensor = torch.from_numpy(
np.array(mask)).float() / 255.0
masks.append(mask_tensor)
labels.append(obj_info.get('category_id', 0))
if masks:
masks = torch.stack(masks, dim=0)
else:
masks = torch.zeros(1, *self.image_size)
labels = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.long)
targets.append({
'masks': masks,
'labels': labels,
'image_id': frame_idx
})
return {
'frames': torch.stack(frames),
'targets': targets,
'video_id': video_name
}
class DVISPlusPlusTrainer:
"""Trainer for DVIS++"""
def __init__(
self,
model: nn.Module,
train_loader: DataLoader,
val_loader: DataLoader,
num_epochs: int = 100,
learning_rate: float = 1e-4,
weight_decay: float = 5e-2,
device: str = 'cuda',
checkpoint_dir: str = './checkpoints',
log_dir: str = './logs'
):
self.model = model.to(device)
self.train_loader = train_loader
self.val_loader = val_loader
self.num_epochs = num_epochs
self.device = device
self.checkpoint_dir = Path(checkpoint_dir)
self.log_dir = Path(log_dir)
# Create directories
self.checkpoint_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
self.log_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# Optimizer
self.optimizer = optim.AdamW(
model.parameters(),
lr=learning_rate,
weight_decay=weight_decay
)
# Learning rate scheduler
self.scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(
self.optimizer, T_max=num_epochs
)
# Logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[
logging.FileHandler(self.log_dir / 'training.log'),
logging.StreamHandler()
]
)
self.best_val_loss = float('inf')
self.global_step = 0
def train_epoch(self) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""Train for one epoch"""
self.model.train()
epoch_losses = {}
pbar = tqdm(self.train_loader, desc='Training')
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(pbar):
frames = [f.to(self.device) for f in batch['frames']]
targets = [[t.to(self.device) for t in target_list]
for target_list in batch['targets']]
# Forward pass
try:
outputs = self.model(frames, targets=targets)
losses = self.model.compute_loss(outputs, targets)
total_loss = losses['total_loss']
# Backward pass
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
total_loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
self.optimizer.step()
# Logging
for key, val in losses.items():
if key not in epoch_losses:
epoch_losses[key] = []
epoch_losses[key].append(val.item())
pbar.set_postfix({
'loss': total_loss.item(),
'step': self.global_step
})
self.global_step += 1
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error in batch {batch_idx}: {str(e)}")
continue
# Average losses
for key in epoch_losses:
epoch_losses[key] = np.mean(epoch_losses[key])
return epoch_losses
@torch.no_grad()
def validate(self) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""Validation loop"""
self.model.eval()
val_losses = {}
pbar = tqdm(self.val_loader, desc='Validation')
for batch in pbar:
frames = [f.to(self.device) for f in batch['frames']]
targets = [[t.to(self.device) for t in target_list]
for target_list in batch['targets']]
try:
outputs = self.model(frames, targets=targets)
losses = self.model.compute_loss(outputs, targets)
for key, val in losses.items():
if key not in val_losses:
val_losses[key] = []
val_losses[key].append(val.item())
pbar.set_postfix({
'val_loss': losses['total_loss'].item()
})
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Validation error: {str(e)}")
continue
# Average losses
for key in val_losses:
val_losses[key] = np.mean(val_losses[key])
return val_losses
def train(self):
"""Full training loop"""
logger.info("Starting training...")
for epoch in range(self.num_epochs):
logger.info(f"\nEpoch {epoch + 1}/{self.num_epochs}")
# Train
train_losses = self.train_epoch()
logger.info(f"Train losses: {train_losses}")
# Validate
val_losses = self.validate()
logger.info(f"Val losses: {val_losses}")
# Learning rate scheduling
self.scheduler.step()
# Checkpoint
if val_losses.get('total_loss', float('inf')) < self.best_val_loss:
self.best_val_loss = val_losses['total_loss']
self.save_checkpoint(epoch, is_best=True)
logger.info(f"Saved best checkpoint at epoch {epoch + 1}")
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
self.save_checkpoint(epoch, is_best=False)
def save_checkpoint(self, epoch: int, is_best: bool = False):
"""Save model checkpoint"""
checkpoint = {
'epoch': epoch,
'model_state': self.model.state_dict(),
'optimizer_state': self.optimizer.state_dict(),
'scheduler_state': self.scheduler.state_dict(),
'global_step': self.global_step,
}
if is_best:
path = self.checkpoint_dir / 'best_model.pt'
else:
path = self.checkpoint_dir / f'checkpoint_epoch_{epoch}.pt'
torch.save(checkpoint, path)
def load_checkpoint(self, checkpoint_path: str):
"""Load model checkpoint"""
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location=self.device)
self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state'])
self.optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_state'])
self.scheduler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['scheduler_state'])
self.global_step = checkpoint['global_step']
logger.info(f"Loaded checkpoint from {checkpoint_path}")
def create_dummy_dataset(num_videos=10, num_frames_per_video=20,
num_objects=5, image_size=(512, 512)):
"""Create a dummy dataset for testing"""
from PIL import Image
import tempfile
import os
temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
video_dir = Path(temp_dir) / 'videos'
video_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
annotations = []
for vid_id in range(num_videos):
video_name = f'video_{vid_id:04d}'
video_path = video_dir / video_name
video_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
frames_info = []
for frame_id in range(num_frames_per_video):
# Create dummy frame
img = Image.new('RGB', image_size,
color=(np.random.randint(0, 256),
np.random.randint(0, 256),
np.random.randint(0, 256)))
img.save(video_path / f'{frame_id:06d}.jpg')
# Create dummy masks
frame_objects = {}
for obj_id in range(num_objects):
mask = Image.new('L', image_size,
color=np.random.randint(0, 256))
mask.save(video_path / f'mask_{frame_id:06d}_{obj_id}.png')
frame_objects[str(obj_id)] = {'category_id': obj_id % 10}
frames_info.append({'objects': frame_objects})
annotations.append({
'video_id': video_name,
'frames': frames_info
})
# Save annotations
anno_file = Path(temp_dir) / 'annotations.json'
with open(anno_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(annotations, f)
return temp_dir, str(anno_file)
# Example usage
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create dummy dataset
data_dir, anno_file = create_dummy_dataset(num_videos=4)
# Create dataset and dataloader
dataset = VideoSegmentationDataset(
video_dir=data_dir + '/videos',
anno_file=anno_file,
num_frames=5,
split='train'
)
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=2,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0
)
# Create model
from dvis_pp import DVISPlusPlus
model = DVISPlusPlus(
num_classes=80,
num_queries=100,
num_frames=5,
backbone_depth=50,
use_contrastive_loss=True,
use_denoising_training=True
)
# Create trainer
trainer = DVISPlusPlusTrainer(
model=model,
train_loader=dataloader,
val_loader=dataloader,
num_epochs=2,
device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
)
# Train
trainer.train()"""
Core model components for DVIS++:
- Segmenter (based on Mask2Former)
- Referring Tracker
- Temporal Refiner
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
import torchvision.models as models
from .utils import (
MultiHeadAttention, FeedForward, get_clones, ContrastiveLoss,
TemporalWeighting, NoiseSimulator
)
class ResNetBackbone(nn.Module):
"""ResNet backbone for feature extraction"""
def __init__(self, depth=50, pretrained=True):
super().__init__()
if depth == 50:
backbone = models.resnet50(pretrained=pretrained)
elif depth == 101:
backbone = models.resnet101(pretrained=pretrained)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported depth: {depth}")
# Remove classification head
self.conv1 = backbone.conv1
self.bn1 = backbone.bn1
self.relu = backbone.relu
self.maxpool = backbone.maxpool
self.layer1 = backbone.layer1
self.layer2 = backbone.layer2
self.layer3 = backbone.layer3
self.layer4 = backbone.layer4
def forward(self, x):
"""Extract multi-scale features"""
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
c1 = self.layer1(x)
c2 = self.layer2(c1)
c3 = self.layer3(c2)
c4 = self.layer4(c3)
return {'c1': c1, 'c2': c2, 'c3': c3, 'c4': c4}
class SegmenterHead(nn.Module):
"""Mask2Former-style segmentation head"""
def __init__(self, in_channels=256, num_classes=80, num_queries=100):
super().__init__()
self.num_queries = num_queries
self.num_classes = num_classes
# Query embeddings
self.query_embed = nn.Embedding(num_queries, in_channels)
# Transformer decoder
decoder_layer = nn.TransformerDecoderLayer(
d_model=in_channels,
nhead=8,
dim_feedforward=2048,
dropout=0.1,
activation='relu',
batch_first=True
)
self.transformer_decoder = nn.TransformerDecoder(decoder_layer, num_layers=6)
# Prediction heads
self.class_embed = nn.Linear(in_channels, num_classes + 1)
self.bbox_embed = nn.Linear(in_channels, 4)
self.mask_embed = nn.Linear(in_channels, in_channels)
# Mask head
self.mask_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 1, 3, padding=1)
)
def forward(self, features, feature_maps):
"""
Args:
features: [B, C, H, W] feature maps from backbone
feature_maps: Multi-scale features for mask decoding
Returns:
dict with 'pred_logits', 'pred_masks', 'pred_boxes'
"""
B, C, H, W = features.shape
# Flatten spatial dimensions
features_flat = features.flatten(2).permute(0, 2, 1) # [B, HW, C]
# Decoder
query_embed = self.query_embed.weight.unsqueeze(0).expand(B, -1, -1)
decoder_output = self.transformer_decoder(query_embed, features_flat)
# Predictions
pred_logits = self.class_embed(decoder_output) # [B, N, num_classes+1]
pred_boxes = self.bbox_embed(decoder_output) # [B, N, 4]
mask_features = self.mask_embed(decoder_output) # [B, N, C]
# Generate masks
pred_masks = self.mask_head(features) # [B, 1, H, W]
pred_masks = pred_masks.expand(B, self.num_queries, -1, -1) # [B, N, H, W]
return {
'pred_logits': pred_logits,
'pred_boxes': pred_boxes,
'pred_masks': pred_masks,
'mask_features': mask_features
}
class Segmenter(nn.Module):
"""Image segmentation module (Mask2Former-style)"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=80, num_queries=100, backbone_depth=50):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_queries = num_queries
# Feature extraction
self.backbone = ResNetBackbone(depth=backbone_depth, pretrained=True)
# Feature projection
self.proj_c2 = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=1)
self.proj_c3 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, kernel_size=1)
self.proj_c4 = nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, kernel_size=1)
# Segmentation head
self.head = SegmenterHead(in_channels=256, num_classes=num_classes,
num_queries=num_queries)
def forward(self, x):
"""
Args:
x: Input images [B, 3, H, W]
Returns:
dict with segmentation results
"""
# Extract features
features = self.backbone(x)
# Project features
c2 = self.proj_c2(features['c2'])
c3 = self.proj_c3(features['c3'])
c4 = self.proj_c4(features['c4'])
# Use highest resolution features
if c4.shape[-1] != c3.shape[-1]:
c4 = F.interpolate(c4, size=c3.shape[-2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
features_combined = c4 # [B, 256, H/8, W/8]
# Segmentation head
outputs = self.head(features_combined, features)
# Store features for later use
outputs['features'] = features_combined
outputs['backbone_features'] = features
return outputs
class ReferringCrossAttention(nn.Module):
"""Referring Cross-Attention for tracking"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, attn_drop=0.0, proj_drop=0.0):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
self.to_q = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.to_kv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 2)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, id_feat, ref_feat, memory_feat):
"""
Args:
id_feat: Identity features (initial noisy values) [B*N, D]
ref_feat: Reference features (from previous frame) [B*N, D]
memory_feat: Memory features (object features) [B*N, D]
Returns:
Attended features [B*N, D]
"""
# Query from reference, keys/values from memory
q = self.to_q(ref_feat)
k, v = self.to_kv(memory_feat).chunk(2, dim=-1)
# Reshape for multi-head attention
B_N = q.shape[0]
q = q.reshape(B_N, 1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
k = k.reshape(B_N, 1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
v = v.reshape(B_N, 1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
# Attention
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# Output
out = (attn @ v).permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B_N, self.num_heads * self.head_dim)
out = self.proj(out)
out = self.proj_drop(out)
# Residual connection with identity
return id_feat + out
class TransformerDenosingBlock(nn.Module):
"""Transformer Denoising block for tracking"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, mlp_ratio=4.0, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
# Referring cross attention
self.rca = ReferringCrossAttention(dim, num_heads=num_heads,
attn_drop=dropout, proj_drop=dropout)
# Self attention
self.self_attn = MultiHeadAttention(dim, num_heads=num_heads,
attn_drop=dropout, proj_drop=dropout)
# Feed forward
mlp_hidden = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = FeedForward(dim, mlp_hidden, dropout=dropout)
# Normalization
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
def forward(self, id_feat, ref_feat, memory_feat):
"""
Args:
id_feat: Identity features [B*N, D]
ref_feat: Reference features [B*N, D]
memory_feat: Memory features [B*N, D]
Returns:
Updated features [B*N, D]
"""
# Referring cross attention
x = self.norm1(id_feat)
x = self.rca(x, ref_feat, memory_feat)
id_feat = id_feat + x
# Self attention
x = self.norm2(id_feat)
x = x.unsqueeze(1) # Add sequence dimension
x = self.self_attn(x).squeeze(1)
id_feat = id_feat + x
# Feed forward
x = self.norm3(id_feat)
x = self.mlp(x)
id_feat = id_feat + x
return id_feat
class ReferringTracker(nn.Module):
"""Referring Tracker for frame-to-frame object tracking"""
def __init__(self, dim=256, num_heads=8, num_layers=6, num_queries=100):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_queries = num_queries
# Denoising blocks
self.denoising_blocks = nn.ModuleList([
TransformerDenosingBlock(dim, num_heads=num_heads)
for _ in range(num_layers)
])
# Reference transformation
self.ref_proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.mlp_ref = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(dim, dim * 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(dim * 2, dim)
)
def forward(self, ref_prev, q_seg, q_noised):
"""
Args:
ref_prev: Previous reference features [B, N, D]
q_seg: Segmented object features [B, N, D]
q_noised: Noised object features [B, N, D]
Returns:
q_rt: Tracked object features [B, N, D]
ref_cur: Current reference features [B, N, D]
"""
B, N, D = q_seg.shape
# Reshape for processing
id_feat = q_noised.reshape(-1, D) # [B*N, D]
ref_feat = ref_prev.reshape(-1, D) # [B*N, D]
memory_feat = q_seg.reshape(-1, D) # [B*N, D]
# Process through denoising blocks
for block in self.denoising_blocks:
id_feat = block(id_feat, ref_feat, memory_feat)
# Reshape back
q_rt = id_feat.reshape(B, N, D)
# Generate new reference
ref_cur = self.ref_proj(q_rt)
ref_cur = ref_cur + self.mlp_ref(ref_cur)
return q_rt, ref_cur
class TemporalDecoderBlock(nn.Module):
"""Temporal decoder block for spatio-temporal modeling"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=8, mlp_ratio=4.0, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
# Short-term temporal convolution
self.short_term_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv1d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
)
# Long-term temporal self-attention
self.long_term_attn = MultiHeadAttention(dim, num_heads=num_heads,
attn_drop=dropout, proj_drop=dropout)
# Cross attention to original features
self.cross_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(dim, num_heads, dropout=dropout,
batch_first=True)
# Feed forward
mlp_hidden = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = FeedForward(dim, mlp_hidden, dropout=dropout)
# Normalization
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.norm4 = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
def forward(self, x, x_seg):
"""
Args:
x: Temporal features [B, N, T, D]
x_seg: Original segmentation features [B, N, T, D]
Returns:
Updated temporal features [B, N, T, D]
"""
B, N, T, D = x.shape
# Short-term temporal convolution
x_short = x.reshape(B * N, D, T)
x_short = self.short_term_conv(x_short)
x_short = x_short.reshape(B, N, D, T).permute(0, 1, 3, 2) # [B, N, T, D]
x = x + x_short
# Long-term temporal self-attention
x_long = x.reshape(B * N, T, D)
x_long = self.long_term_attn(x_long)
x = x + x_long.reshape(B, N, T, D)
# Cross attention to original features
x_cross = x.reshape(B * N, T, D)
x_seg_cross = x_seg.reshape(B * N, T, D)
x_cross, _ = self.cross_attn(x_cross, x_seg_cross, x_seg_cross)
x = x + x_cross.reshape(B, N, T, D)
# Feed forward
x_ff = x.reshape(B * N, T, D)
x_ff = self.norm4(x_ff)
x_ff = self.mlp(x_ff)
x = x + x_ff.reshape(B, N, T, D)
return x
class TemporalRefiner(nn.Module):
"""Temporal refiner for spatio-temporal feature modeling"""
def __init__(self, dim=256, num_heads=8, num_layers=6):
super().__init__()
self.decoder_layers = nn.ModuleList([
TemporalDecoderBlock(dim, num_heads=num_heads)
for _ in range(num_layers)
])
self.temporal_weighting = TemporalWeighting(dim)
def forward(self, q_rt, q_seg):
"""
Args:
q_rt: Referred tracked features [B, N, T, D]
q_seg: Original segmentation features [B, N, T, D]
Returns:
q_tr: Temporal refined features [B, N, T, D]
q_tr_weighted: Category-level representation [B, N, D]
"""
x = q_rt
# Process through temporal decoder layers
for layer in self.decoder_layers:
x = layer(x, q_seg)
q_tr = x
# Compute category-level representation via temporal weighting
B, N, T, D = q_tr.shape
q_tr_weighted = self.temporal_weighting(q_tr) # [B, N, D]
return q_tr, q_tr_weighted
class DVISPPSegmentationHead(nn.Module):
"""Segmentation head for mask and class prediction"""
def __init__(self, dim=256, num_classes=80):
super().__init__()
self.mask_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(dim, 1, 3, padding=1)
)
self.class_head = nn.Linear(dim, num_classes + 1)
def forward(self, features, class_features, feature_maps):
"""
Args:
features: Spatial features [B, N, D] or [B, D, H, W]
class_features: Features for classification [B, N, D]
feature_maps: Feature maps for mask generation [B, C, H, W]
Returns:
dict with masks and logits
"""
# Generate masks
if len(features.shape) == 4:
masks = self.mask_head(features)
else:
# Reshape for mask head if needed
B, N, D = features.shape
masks = torch.zeros(B, N, feature_maps.shape[-2], feature_maps.shape[-1],
device=features.device)
for i in range(N):
masks[:, i:i+1] = self.mask_head(feature_maps)
# Generate class logits
class_logits = self.class_head(class_features)
return {
'masks': masks,
'logits': class_logits
}"""
Main entry point and example usage for DVIS++
"""
import torch
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
import argparse
import logging
from typing import List
import cv2
from dvis_pp import DVISPlusPlus, DVISPlusPlusWithClip
from training import DVISPlusPlusTrainer, VideoSegmentationDataset, create_dummy_dataset
from inference import DVISPlusPlusInference, SegmentationEvaluator, PostProcessor
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class DVISPlusPlusDemo:
"""Complete demo for DVIS++"""
def __init__(self, device: str = 'cuda'):
self.device = device
logger.info(f"Using device: {device}")
def create_model(
self,
num_classes: int = 80,
num_queries: int = 100,
use_clip: bool = False,
pretrained_path: str = None
) -> DVISPlusPlus:
"""Create DVIS++ model"""
if use_clip:
model = DVISPlusPlusWithClip(
num_classes=num_classes,
num_queries=num_queries,
num_frames=5
)
logger.info("Created DVIS++ with CLIP")
else:
model = DVISPlusPlus(
num_classes=num_classes,
num_queries=num_queries,
num_frames=5,
backbone_depth=50,
use_contrastive_loss=True,
use_denoising_training=True
)
logger.info("Created DVIS++")
if pretrained_path:
checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path, map_location=self.device)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state'])
logger.info(f"Loaded pretrained weights from {pretrained_path}")
return model.to(self.device)
def train(
self,
data_dir: str,
anno_file: str,
num_epochs: int = 100,
batch_size: int = 2,
learning_rate: float = 1e-4,
checkpoint_dir: str = './checkpoints'
):
"""Train DVIS++"""
logger.info("Starting training...")
# Create dataset
train_dataset = VideoSegmentationDataset(
video_dir=data_dir,
anno_file=anno_file,
num_frames=5,
split='train'
)
val_dataset = VideoSegmentationDataset(
video_dir=data_dir,
anno_file=anno_file,
num_frames=5,
split='val'
)
train_loader = DataLoader(
train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=4
)
val_loader = DataLoader(
val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=4
)
# Create model
model = self.create_model()
# Create trainer
trainer = DVISPlusPlusTrainer(
model=model,
train_loader=train_loader,
val_loader=val_loader,
num_epochs=num_epochs,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
device=self.device,
checkpoint_dir=checkpoint_dir
)
# Train
trainer.train()
return trainer
def inference(
self,
video_path: str,
checkpoint_path: str,
confidence_threshold: float = 0.5,
output_dir: str = './inference_output'
):
"""Run inference on video"""
logger.info(f"Running inference on {video_path}")
# Load model
model = self.create_model(pretrained_path=checkpoint_path)
model.eval()
# Load video frames
frames = self._load_video(video_path)
logger.info(f"Loaded {len(frames)} frames")
# Inference
inferencer = DVISPlusPlusInference(
model=model,
device=self.device,
confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold
)
results = inferencer.segment_video(frames)
logger.info(f"Segmented {results['num_frames']} frames")
# Visualize
inferencer.visualize_results(frames, results, output_dir)
return results
def inference_on_image_sequence(
self,
image_dir: str,
checkpoint_path: str,
num_frames: int = 5,
confidence_threshold: float = 0.5,
output_dir: str = './inference_output'
):
"""Run inference on image sequence"""
logger.info(f"Running inference on image sequence in {image_dir}")
# Load images
image_paths = sorted(Path(image_dir).glob('*.jpg')) + \
sorted(Path(image_dir).glob('*.png'))
image_paths = image_paths[:num_frames]
frames = [cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(str(p)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
for p in image_paths]
logger.info(f"Loaded {len(frames)} images")
# Run inference
return self.inference_internal(
frames=frames,
checkpoint_path=checkpoint_path,
confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold,
output_dir=output_dir
)
def inference_internal(
self,
frames: List[np.ndarray],
checkpoint_path: str,
confidence_threshold: float = 0.5,
output_dir: str = './inference_output'
):
"""Internal inference function"""
# Load model
model = self.create_model(pretrained_path=checkpoint_path)
model.eval()
# Inference
inferencer = DVISPlusPlusInference(
model=model,
device=self.device,
confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold
)
results = inferencer.segment_video(frames)
# Visualize
inferencer.visualize_results(frames, results, output_dir)
return results
def evaluate(
self,
data_dir: str,
anno_file: str,
checkpoint_path: str,
batch_size: int = 2
) -> dict:
"""Evaluate model on dataset"""
logger.info("Starting evaluation...")
# Load model
model = self.create_model(pretrained_path=checkpoint_path)
model.eval()
# Create dataset
val_dataset = VideoSegmentationDataset(
video_dir=data_dir,
anno_file=anno_file,
num_frames=5,
split='val'
)
val_loader = DataLoader(
val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=4
)
# Evaluate
evaluator = SegmentationEvaluator()
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(val_loader):
frames = [f.to(self.device) for f in batch['frames']]
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(frames)
# Add predictions and ground truth
for t, pred in enumerate(outputs['predictions']):
masks = pred['masks'].sigmoid().cpu().numpy()
logits = pred['logits'].cpu().numpy()
evaluator.add_prediction(
masks=masks,
class_ids=logits.argmax(-1),
scores=logits.max(-1),
image_id=batch_idx * len(frames) + t
)
if batch_idx >= 10: # Limit evaluation for demo
break
# Compute metrics
metrics = evaluator.compute_metrics()
logger.info(f"Evaluation metrics: {metrics.to_dict()}")
return metrics.to_dict()
@staticmethod
def _load_video(video_path: str, max_frames: int = 100) -> List[np.ndarray]:
"""Load video frames"""
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
frames = []
while len(frames) < max_frames:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
frames.append(frame)
cap.release()
return frames
def test_model_forward_pass(self):
"""Test model forward pass"""
logger.info("Testing model forward pass...")
model = self.create_model()
model.eval()
# Create dummy input
batch_size = 2
num_frames = 5
height, width = 512, 512
frames = [
torch.randn(batch_size, 3, height, width).to(self.device)
for _ in range(num_frames)
]
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(frames)
logger.info("✓ Forward pass successful")
logger.info(f" Output keys: {outputs.keys()}")
logger.info(f" Number of predictions: {len(outputs['predictions'])}")
return outputs
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='DVIS++ demo')
parser.add_argument('--mode', type=str, default='test',
choices=['test', 'train', 'inference', 'evaluate'],
help='Mode to run')
parser.add_argument('--data-dir', type=str, help='Data directory')
parser.add_argument('--anno-file', type=str, help='Annotation file')
parser.add_argument('--checkpoint', type=str, help='Checkpoint path')
parser.add_argument('--video-path', type=str, help='Video path for inference')
parser.add_argument('--image-dir', type=str, help='Image directory for inference')
parser.add_argument('--output-dir', type=str, default='./output',
help='Output directory')
parser.add_argument('--num-epochs', type=int, default=100,
help='Number of training epochs')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=2,
help='Batch size')
parser.add_argument('--device', type=str, default='cuda',
help='Device to use')
args = parser.parse_args()
# Create demo
demo = DVISPlusPlusDemo(device=args.device)
if args.mode == 'test':
logger.info("=" * 80)
logger.info("DVIS++ Model Test")
logger.info("=" * 80)
demo.test_model_forward_pass()
elif args.mode == 'train':
logger.info("=" * 80)
logger.info("DVIS++ Training")
logger.info("=" * 80)
if not args.data_dir or not args.anno_file:
# Create dummy dataset for demo
logger.info("Creating dummy dataset...")
data_dir, anno_file = create_dummy_dataset()
args.data_dir = data_dir + '/videos'
args.anno_file = anno_file
demo.train(
data_dir=args.data_dir,
anno_file=args.anno_file,
num_epochs=args.num_epochs,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
checkpoint_dir=args.output_dir
)
elif args.mode == 'inference':
logger.info("=" * 80)
logger.info("DVIS++ Inference")
logger.info("=" * 80)
if args.video_path:
results = demo.inference(
video_path=args.video_path,
checkpoint_path=args.checkpoint,
output_dir=args.output_dir
)
elif args.image_dir:
results = demo.inference_on_image_sequence(
image_dir=args.image_dir,
checkpoint_path=args.checkpoint,
output_dir=args.output_dir
)
else:
logger.error("Please provide either --video-path or --image-dir")
elif args.mode == 'evaluate':
logger.info("=" * 80)
logger.info("DVIS++ Evaluation")
logger.info("=" * 80)
if not args.data_dir or not args.anno_file:
logger.error("Please provide --data-dir and --anno-file")
else:
metrics = demo.evaluate(
data_dir=args.data_dir,
anno_file=args.anno_file,
checkpoint_path=args.checkpoint,
batch_size=args.batch_size
)
logger.info("=" * 80)
logger.info("Done!")
logger.info("=" * 80)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()"""
Complete DVIS++ model implementation
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
from .models import Segmenter, ReferringTracker, TemporalRefiner, DVISPPSegmentationHead
from .utils import (
NoiseSimulator, ContrastiveLoss, MemoryBank, HungarianMatcher,
compute_dice_loss, compute_sigmoid_focal_loss
)
class DVISPlusPlus(nn.Module):
"""Complete DVIS++ framework"""
def __init__(
self,
num_classes: int = 80,
num_queries: int = 100,
num_frames: int = 5,
backbone_depth: int = 50,
hidden_dim: int = 256,
num_heads: int = 8,
num_tracker_layers: int = 6,
num_refiner_layers: int = 6,
pretrained_backbone: bool = True,
use_contrastive_loss: bool = True,
use_denoising_training: bool = True
):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_queries = num_queries
self.num_frames = num_frames
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.use_contrastive_loss = use_contrastive_loss
self.use_denoising_training = use_denoising_training
# Components
self.segmenter = Segmenter(
num_classes=num_classes,
num_queries=num_queries,
backbone_depth=backbone_depth
)
self.referring_tracker = ReferringTracker(
dim=hidden_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
num_layers=num_tracker_layers,
num_queries=num_queries
)
self.temporal_refiner = TemporalRefiner(
dim=hidden_dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
num_layers=num_refiner_layers
)
self.segmentation_head = DVISPPSegmentationHead(
dim=hidden_dim,
num_classes=num_classes
)
# Noise simulator
if self.use_denoising_training:
self.noise_simulator = NoiseSimulator()
else:
self.noise_simulator = None
# Matching
self.matcher = HungarianMatcher(cost_class=1, cost_mask=1, cost_dice=1)
# Contrastive learning
if self.use_contrastive_loss:
self.contrastive_loss_fn = ContrastiveLoss(temperature=0.07)
self.memory_bank = MemoryBank(capacity=4096, dim=hidden_dim)
else:
self.contrastive_loss_fn = None
self.memory_bank = None
def initialize_references(self, q_seg):
"""Initialize references from first frame segmentation"""
B, N, D = q_seg.shape
# Simple MLP transformation for reference initialization
ref = nn.Linear(D, D)(q_seg)
return ref
def forward_segmenter(self, frame):
"""Forward pass through segmenter"""
return self.segmenter(frame)
def forward_tracker(self, ref_prev, q_seg, apply_noise=False):
"""Forward pass through referring tracker"""
if apply_noise and self.training and self.noise_simulator is not None:
q_noised = self.noise_simulator(q_seg, strategy='weighted_avg', prob=0.8)
else:
q_noised = q_seg
q_rt, ref_cur = self.referring_tracker(ref_prev, q_seg, q_noised)
return q_rt, ref_cur
def forward_refiner(self, q_rt_sequence, q_seg_sequence):
"""Forward pass through temporal refiner"""
# Stack temporal features
B, N, D = q_rt_sequence[0].shape
T = len(q_rt_sequence)
q_rt_stacked = torch.stack(q_rt_sequence, dim=2) # [B, N, T, D]
q_seg_stacked = torch.stack(q_seg_sequence, dim=2) # [B, N, T, D]
q_tr, q_tr_weighted = self.temporal_refiner(q_rt_stacked, q_seg_stacked)
return q_tr, q_tr_weighted
def forward(
self,
frames: List[torch.Tensor],
targets: Optional[List[Dict]] = None,
return_intermediate: bool = False
) -> Dict:
"""
Forward pass for video segmentation
Args:
frames: List of T frames [B, 3, H, W]
targets: Optional ground truth for training
return_intermediate: Whether to return intermediate predictions
Returns:
dict with segmentation results
"""
T = len(frames)
device = frames[0].device
# Process first frame through segmenter
seg_out_0 = self.forward_segmenter(frames[0])
B = frames[0].shape[0]
N = self.num_queries
D = self.hidden_dim
# Initialize tracking variables
q_seg_sequence = [seg_out_0.get('mask_features',
torch.zeros(B, N, D, device=device))]
q_rt_sequence = [q_seg_sequence[0].clone()]
ref_prev = self.initialize_references(q_seg_sequence[0])
refs = [ref_prev]
intermediate_results = {
'predictions': [seg_out_0],
'tracked_features': [q_rt_sequence[0]],
'references': [ref_prev]
}
# Process remaining frames
for t in range(1, T):
# Segmentation
seg_out_t = self.forward_segmenter(frames[t])
q_seg_t = seg_out_t.get('mask_features',
torch.zeros(B, N, D, device=device))
q_seg_sequence.append(q_seg_t)
# Tracking
q_rt_t, ref_cur = self.forward_tracker(
ref_prev, q_seg_t, apply_noise=(t > 0)
)
q_rt_sequence.append(q_rt_t)
refs.append(ref_cur)
ref_prev = ref_cur
intermediate_results['predictions'].append(seg_out_t)
intermediate_results['tracked_features'].append(q_rt_t)
intermediate_results['references'].append(ref_cur)
# Temporal refinement
q_tr, q_tr_weighted = self.forward_refiner(q_rt_sequence, q_seg_sequence)
# Generate final predictions
final_predictions = []
for t in range(T):
seg_out = intermediate_results['predictions'][t]
features = seg_out.get('features',
torch.zeros(B, D, 32, 32, device=device))
# Use refined features for prediction
pred = self.segmentation_head(
features,
q_tr_weighted, # Use weighted category representation
features
)
final_predictions.append(pred)
outputs = {
'predictions': final_predictions,
'intermediate': intermediate_results if return_intermediate else None,
'references': refs,
'tracked_features_sequence': q_rt_sequence,
'refined_features': q_tr,
'refined_weighted': q_tr_weighted
}
return outputs
def compute_loss(
self,
outputs: Dict,
targets: List[Dict],
loss_weights: Optional[Dict] = None
) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""
Compute training loss
Args:
outputs: Model outputs
targets: Ground truth targets
loss_weights: Loss weights
Returns:
dict with individual loss terms
"""
if loss_weights is None:
loss_weights = {
'mask': 1.0,
'class': 1.0,
'dice': 5.0,
'contrastive_seg': 2.0,
'contrastive_tracker': 0.7,
'contrastive_refiner': 0.5
}
total_loss = 0.0
loss_dict = {}
# Segmentation losses
predictions = outputs['predictions']
B = predictions[0]['masks'].shape[0]
# Compute losses for each frame
for t, (pred, target) in enumerate(zip(predictions, targets)):
# Classification loss
pred_logits = pred['logits']
target_classes = torch.cat([v['labels'] for v in target])
loss_ce = F.cross_entropy(pred_logits.flatten(0, 1),
target_classes,
reduction='mean')
loss_dict[f'class_t{t}'] = loss_ce
total_loss += loss_weights['class'] * loss_ce
# Mask loss
pred_masks = pred['masks']
target_masks = torch.cat([v['masks'] for v in target])
# Dice loss
pred_masks_sigmoid = pred_masks.sigmoid()
loss_dice = compute_dice_loss(pred_masks_sigmoid, target_masks)
loss_dict[f'dice_t{t}'] = loss_dice
total_loss += loss_weights['dice'] * loss_dice
# Mask loss (BCE)
loss_bce = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
pred_masks, target_masks, reduction='mean'
)
loss_dict[f'mask_t{t}'] = loss_bce
total_loss += loss_weights['mask'] * loss_bce
# Contrastive losses (if enabled)
if self.use_contrastive_loss and self.training:
# Segmenter contrastive loss
tracked_features = outputs['tracked_features_sequence']
if len(tracked_features) > 1:
anchor = tracked_features[0] # [B, N, D]
positive = tracked_features[1] # [B, N, D]
# Create contrastive batch
B, N, D = anchor.shape
anchor_flat = anchor.reshape(-1, D)
positive_flat = positive.reshape(-1, D)
# Dummy negatives (from memory bank if available)
if self.memory_bank is not None:
negatives = self.memory_bank.get()[:B*N].reshape(B*N, -1)
if negatives.shape[1] != D:
negatives = negatives[:, :D]
else:
negatives = torch.roll(positive_flat, shifts=1, dims=0).unsqueeze(1)
loss_contrastive = self.contrastive_loss_fn(
anchor_flat,
positive_flat.unsqueeze(1),
negatives.unsqueeze(1) if len(negatives.shape) == 2
else negatives
)
loss_dict['contrastive_seg'] = loss_contrastive
total_loss += loss_weights['contrastive_seg'] * loss_contrastive
loss_dict['total_loss'] = total_loss
return loss_dict
def inference(
self,
frames: List[torch.Tensor],
confidence_threshold: float = 0.5
) -> Dict:
"""
Inference mode (no gradients)
Args:
frames: List of video frames
confidence_threshold: Threshold for predictions
Returns:
Segmentation results
"""
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self.forward(frames, targets=None, return_intermediate=False)
# Process outputs
results = []
for t, pred in enumerate(outputs['predictions']):
masks = pred['masks'].sigmoid()
logits = pred['logits']
# Filter by confidence
conf = logits.softmax(-1).max(-1)[0]
valid = conf > confidence_threshold
result = {
'masks': masks[valid],
'logits': logits[valid],
'confidence': conf[valid],
'frame_id': t
}
results.append(result)
return {'video_results': results, 'frame_count': len(frames)}
class DVISPlusPlusWithClip(DVISPlusPlus):
"""DVIS++ with CLIP integration for open-vocabulary segmentation"""
def __init__(self, *args, clip_model_name='ViT-B/32', **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
try:
import clip
self.clip_model, self.clip_processor = clip.load(clip_model_name)
self.clip_model.eval()
for param in self.clip_model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
except ImportError:
print("CLIP not available. Install with: pip install clip")
self.clip_model = None
self.clip_processor = None
def get_text_embeddings(self, class_names: List[str]) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Get CLIP text embeddings for class names"""
if self.clip_model is None:
raise RuntimeError("CLIP model not loaded")
with torch.no_grad():
text_tokens = clip.tokenize(class_names)
text_embeddings = self.clip_model.encode_text(text_tokens)
return text_embeddings
def forward_ov(
self,
frames: List[torch.Tensor],
class_names: List[str]
) -> Dict:
"""Forward pass with open-vocabulary support"""
# Standard forward pass
outputs = self.forward(frames)
# Get text embeddings
text_embeddings = self.get_text_embeddings(class_names)
# Match visual features to text embeddings
for t, pred in enumerate(outputs['predictions']):
visual_features = outputs['refined_weighted'] # [B, N, D]
# Simple cosine similarity matching
visual_normalized = F.normalize(visual_features, dim=-1)
text_normalized = F.normalize(text_embeddings, dim=-1)
similarities = torch.matmul(visual_normalized, text_normalized.T)
pred['ov_logits'] = similarities
return outputs"""
Inference utilities and evaluation metrics for DVIS++
"""
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
from dataclasses import dataclass
import json
@dataclass
class SegmentationMetrics:
"""Container for segmentation metrics"""
ap: float
ap50: float
ap75: float
ar1: float
ar10: float
def to_dict(self) -> Dict:
return {
'AP': self.ap,
'AP50': self.ap50,
'AP75': self.ap75,
'AR1': self.ar1,
'AR10': self.ar10
}
class DVISPlusPlusInference:
"""Inference module for DVIS++"""
def __init__(
self,
model,
device: str = 'cuda',
confidence_threshold: float = 0.5,
min_mask_area: int = 100
):
self.model = model.to(device).eval()
self.device = device
self.confidence_threshold = confidence_threshold
self.min_mask_area = min_mask_area
@torch.no_grad()
def segment_video(
self,
frames: List[np.ndarray]
) -> Dict:
"""
Segment video frames
Args:
frames: List of video frames as numpy arrays [H, W, 3]
Returns:
Segmentation results
"""
# Convert to tensors
device = self.device
frame_tensors = []
for frame in frames:
# Normalize
frame_tensor = torch.from_numpy(frame).float().permute(2, 0, 1) / 255.0
# Standardize
frame_tensor[0] = (frame_tensor[0] - 0.485) / 0.229
frame_tensor[1] = (frame_tensor[1] - 0.456) / 0.224
frame_tensor[2] = (frame_tensor[2] - 0.406) / 0.225
frame_tensors.append(frame_tensor.to(device))
# Forward pass
outputs = self.model(frame_tensors)
# Process predictions
results = []
for t, pred in enumerate(outputs['predictions']):
masks = pred['masks'].sigmoid()
logits = pred['logits']
# Get class predictions
class_probs = logits.softmax(-1)
class_ids = class_probs.argmax(-1)
confidence = class_probs.max(-1)[0]
# Filter by confidence
valid_mask = confidence[0] > self.confidence_threshold
frame_result = {
'masks': masks[0][valid_mask].cpu().numpy(),
'class_ids': class_ids[0][valid_mask].cpu().numpy(),
'confidence': confidence[0][valid_mask].cpu().numpy(),
'frame_id': t
}
results.append(frame_result)
return {
'video_results': results,
'num_frames': len(frames)
}
@torch.no_grad()
def segment_frame(self, frame: np.ndarray) -> Dict:
"""Segment a single frame"""
# This would use just one frame with zero-padding for other frames
results = self.segment_video([frame] * self.model.num_frames)
return results['video_results'][0]
def visualize_results(
self,
frames: List[np.ndarray],
results: Dict,
output_dir: str = './vis_output'
):
"""Visualize segmentation results"""
output_dir = Path(output_dir)
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
for t, (frame, result) in enumerate(zip(frames, results['video_results'])):
# Create visualization
vis_frame = frame.copy()
# Draw masks
masks = result['masks']
class_ids = result['class_ids']
confidence = result['confidence']
colors = self._get_colors(len(masks))
for mask_id, (mask, class_id, conf) in enumerate(
zip(masks, class_ids, confidence)
):
color = colors[mask_id]
# Resize mask to frame size
mask_resized = cv2.resize(
mask, (frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0]),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR
)
# Apply mask
vis_frame[mask_resized > 0.5] = (
0.7 * vis_frame[mask_resized > 0.5] +
0.3 * np.array(color)
)
# Draw contour
contour = (mask_resized > 0.5).astype(np.uint8) * 255
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(
contour, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE
)
cv2.drawContours(vis_frame, contours, -1, color, 2)
# Add label
if len(contours) > 0:
M = cv2.moments(contours[0])
if M['m00'] > 0:
cx = int(M['m10'] / M['m00'])
cy = int(M['m01'] / M['m00'])
cv2.putText(
vis_frame,
f'ID: {mask_id} ({conf:.2f})',
(cx, cy),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.5,
color,
2
)
# Save visualization
output_path = output_dir / f'frame_{t:06d}.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(str(output_path), cv2.cvtColor(vis_frame.astype(np.uint8),
cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
print(f"Visualizations saved to {output_dir}")
@staticmethod
def _get_colors(num_colors: int) -> List[Tuple[int, int, int]]:
"""Generate distinct colors"""
colors = []
for i in range(num_colors):
hue = int((i / num_colors) * 180)
hsv = np.uint8([[[hue, 255, 255]]])
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)[0][0]
colors.append(tuple(int(x) for x in rgb))
return colors
class SegmentationEvaluator:
"""Evaluation metrics for video segmentation"""
def __init__(self):
self.predictions = []
self.ground_truths = []
def add_prediction(
self,
masks: np.ndarray,
class_ids: np.ndarray,
scores: np.ndarray,
image_id: int
):
"""Add predictions"""
self.predictions.append({
'masks': masks,
'class_ids': class_ids,
'scores': scores,
'image_id': image_id
})
def add_ground_truth(
self,
masks: np.ndarray,
class_ids: np.ndarray,
image_id: int
):
"""Add ground truth"""
self.ground_truths.append({
'masks': masks,
'class_ids': class_ids,
'image_id': image_id
})
def compute_iou(
self,
mask1: np.ndarray,
mask2: np.ndarray
) -> float:
"""Compute Intersection over Union"""
intersection = np.logical_and(mask1, mask2).sum()
union = np.logical_or(mask1, mask2).sum()
if union == 0:
return 0.0
return intersection / union
def compute_ap(self, iou_threshold: float = 0.5) -> float:
"""Compute Average Precision"""
if not self.predictions or not self.ground_truths:
return 0.0
# Simple AP computation (simplified version)
tp = 0
fp = 0
total_gt = sum(len(gt['masks']) for gt in self.ground_truths)
# Sort predictions by score
sorted_preds = sorted(
self.predictions,
key=lambda x: x['scores'].max() if len(x['scores']) > 0 else 0,
reverse=True
)
matched_gt = set()
for pred in sorted_preds:
pred_masks = pred['masks']
image_id = pred['image_id']
# Find corresponding ground truth
gt_for_image = [gt for gt in self.ground_truths
if gt['image_id'] == image_id]
if not gt_for_image:
fp += len(pred_masks)
continue
gt_masks = gt_for_image[0]['masks']
matched = False
for gt_idx, gt_mask in enumerate(gt_masks):
if (image_id, gt_idx) in matched_gt:
continue
for pred_mask in pred_masks:
iou = self.compute_iou(pred_mask, gt_mask)
if iou > iou_threshold:
tp += 1
matched_gt.add((image_id, gt_idx))
matched = True
break
if not matched:
fp += len(pred_masks)
# Compute precision and recall
precision = tp / (tp + fp) if (tp + fp) > 0 else 0
recall = tp / total_gt if total_gt > 0 else 0
return (2 * precision * recall) / (precision + recall) if (precision + recall) > 0 else 0
def compute_metrics(self) -> SegmentationMetrics:
"""Compute all metrics"""
ap = self.compute_ap(iou_threshold=0.50)
ap50 = self.compute_ap(iou_threshold=0.50)
ap75 = self.compute_ap(iou_threshold=0.75)
ar1 = self.compute_ap(iou_threshold=0.50) # Simplified
ar10 = self.compute_ap(iou_threshold=0.50) # Simplified
return SegmentationMetrics(
ap=ap,
ap50=ap50,
ap75=ap75,
ar1=ar1,
ar10=ar10
)
def save_metrics(self, output_path: str):
"""Save metrics to file"""
metrics = self.compute_metrics()
with open(output_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(metrics.to_dict(), f, indent=2)
class PostProcessor:
"""Post-processing for predictions"""
@staticmethod
def apply_crf(
masks: np.ndarray,
image: np.ndarray,
num_iterations: int = 10
) -> np.ndarray:
"""Apply Conditional Random Field for refinement"""
try:
import pydensecrf.densecrf as dcrf
from pydensecrf.utils import unary_from_softmax
# This is a placeholder - actual CRF implementation would go here
return masks
except ImportError:
print("pydensecrf not available. Skipping CRF refinement.")
return masks
@staticmethod
def temporal_smoothing(
masks_sequence: List[np.ndarray],
window_size: int = 3
) -> List[np.ndarray]:
"""Apply temporal smoothing across video frames"""
smoothed = []
for i, mask in enumerate(masks_sequence):
# Compute average with neighbors
start = max(0, i - window_size // 2)
end = min(len(masks_sequence), i + window_size // 2 + 1)
avg_mask = np.mean(
[masks_sequence[j] for j in range(start, end)],
axis=0
)
smoothed.append(avg_mask)
return smoothed
@staticmethod
def remove_small_objects(
masks: np.ndarray,
min_size: int = 100
) -> np.ndarray:
"""Remove small connected components"""
from scipy import ndimage
filtered_masks = []
for mask in masks:
# Label connected components
labeled, num_features = ndimage.label(mask > 0.5)
# Remove small components
for comp_id in range(1, num_features + 1):
component = (labeled == comp_id)
if component.sum() >= min_size:
filtered_masks.append(mask * component)
if filtered_masks:
return np.stack(filtered_masks)
else:
return np.zeros_like(masks)"""
Configuration and quick start guide for DVIS++
"""
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any
import json
from pathlib import Path
@dataclass
class ModelConfig:
"""Model configuration"""
num_classes: int = 80
num_queries: int = 100
num_frames: int = 5
backbone_depth: int = 50
hidden_dim: int = 256
num_heads: int = 8
num_tracker_layers: int = 6
num_refiner_layers: int = 6
pretrained_backbone: bool = True
use_contrastive_loss: bool = True
use_denoising_training: bool = True
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
'num_classes': self.num_classes,
'num_queries': self.num_queries,
'num_frames': self.num_frames,
'backbone_depth': self.backbone_depth,
'hidden_dim': self.hidden_dim,
'num_heads': self.num_heads,
'num_tracker_layers': self.num_tracker_layers,
'num_refiner_layers': self.num_refiner_layers,
'pretrained_backbone': self.pretrained_backbone,
'use_contrastive_loss': self.use_contrastive_loss,
'use_denoising_training': self.use_denoising_training,
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, config_dict: Dict[str, Any]) -> 'ModelConfig':
return cls(**config_dict)
@dataclass
class TrainingConfig:
"""Training configuration"""
num_epochs: int = 100
batch_size: int = 2
learning_rate: float = 1e-4
weight_decay: float = 5e-2
warmup_epochs: int = 5
num_workers: int = 4
device: str = 'cuda'
checkpoint_dir: str = './checkpoints'
log_dir: str = './logs'
save_interval: int = 10 # Save checkpoint every N epochs
val_interval: int = 1 # Validate every N epochs
# Loss weights
loss_weights: Dict[str, float] = None
def __post_init__(self):
if self.loss_weights is None:
self.loss_weights = {
'mask': 5.0,
'class': 2.0,
'dice': 5.0,
'contrastive_seg': 2.0,
'contrastive_tracker': 0.7,
'contrastive_refiner': 0.5
}
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
'num_epochs': self.num_epochs,
'batch_size': self.batch_size,
'learning_rate': self.learning_rate,
'weight_decay': self.weight_decay,
'warmup_epochs': self.warmup_epochs,
'num_workers': self.num_workers,
'device': self.device,
'checkpoint_dir': self.checkpoint_dir,
'log_dir': self.log_dir,
'save_interval': self.save_interval,
'val_interval': self.val_interval,
'loss_weights': self.loss_weights,
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, config_dict: Dict[str, Any]) -> 'TrainingConfig':
return cls(**config_dict)
@dataclass
class DataConfig:
"""Data configuration"""
video_dir: str = './data/videos'
anno_file: str = './data/annotations.json'
image_size: tuple = (512, 512)
num_frames: int = 5
train_split: float = 0.8
val_split: float = 0.1
test_split: float = 0.1
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
'video_dir': self.video_dir,
'anno_file': self.anno_file,
'image_size': self.image_size,
'num_frames': self.num_frames,
'train_split': self.train_split,
'val_split': self.val_split,
'test_split': self.test_split,
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, config_dict: Dict[str, Any]) -> 'DataConfig':
return cls(**config_dict)
@dataclass
class InferenceConfig:
"""Inference configuration"""
checkpoint_path: str = './checkpoints/best_model.pt'
confidence_threshold: float = 0.5
min_mask_area: int = 100
use_post_processing: bool = True
post_processing_methods: list = None
output_dir: str = './inference_output'
def __post_init__(self):
if self.post_processing_methods is None:
self.post_processing_methods = [
'temporal_smoothing',
'remove_small_objects'
]
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
'checkpoint_path': self.checkpoint_path,
'confidence_threshold': self.confidence_threshold,
'min_mask_area': self.min_mask_area,
'use_post_processing': self.use_post_processing,
'post_processing_methods': self.post_processing_methods,
'output_dir': self.output_dir,
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, config_dict: Dict[str, Any]) -> 'InferenceConfig':
return cls(**config_dict)
class ConfigManager:
"""Manage DVIS++ configurations"""
def __init__(self):
self.model_config = ModelConfig()
self.training_config = TrainingConfig()
self.data_config = DataConfig()
self.inference_config = InferenceConfig()
def save(self, path: str):
"""Save all configurations to JSON file"""
config = {
'model': self.model_config.to_dict(),
'training': self.training_config.to_dict(),
'data': self.data_config.to_dict(),
'inference': self.inference_config.to_dict(),
}
with open(path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(config, f, indent=2)
def load(self, path: str):
"""Load all configurations from JSON file"""
with open(path, 'r') as f:
config = json.load(f)
if 'model' in config:
self.model_config = ModelConfig.from_dict(config['model'])
if 'training' in config:
self.training_config = TrainingConfig.from_dict(config['training'])
if 'data' in config:
self.data_config = DataConfig.from_dict(config['data'])
if 'inference' in config:
self.inference_config = InferenceConfig.from_dict(config['inference'])
def __repr__(self):
return f"""
DVIS++ Configuration:
Model Config:
- Classes: {self.model_config.num_classes}
- Queries: {self.model_config.num_queries}
- Frames: {self.model_config.num_frames}
- Backbone Depth: {self.model_config.backbone_depth}
- Use Contrastive Loss: {self.model_config.use_contrastive_loss}
- Use Denoising: {self.model_config.use_denoising_training}
Training Config:
- Epochs: {self.training_config.num_epochs}
- Batch Size: {self.training_config.batch_size}
- Learning Rate: {self.training_config.learning_rate}
- Device: {self.training_config.device}
Data Config:
- Video Directory: {self.data_config.video_dir}
- Annotation File: {self.data_config.anno_file}
- Image Size: {self.data_config.image_size}
Inference Config:
- Checkpoint: {self.inference_config.checkpoint_path}
- Confidence Threshold: {self.inference_config.confidence_threshold}
"""
# Preset configurations
SMALL_MODEL = ConfigManager()
SMALL_MODEL.model_config = ModelConfig(
num_classes=80,
num_queries=50,
num_frames=3,
backbone_depth=18, # ResNet-18
hidden_dim=128,
)
SMALL_MODEL.training_config.batch_size = 4
SMALL_MODEL.training_config.learning_rate = 5e-4
MEDIUM_MODEL = ConfigManager()
MEDIUM_MODEL.model_config = ModelConfig(
num_classes=80,
num_queries=100,
num_frames=5,
backbone_depth=50,
hidden_dim=256,
)
MEDIUM_MODEL.training_config.batch_size = 2
MEDIUM_MODEL.training_config.learning_rate = 1e-4
LARGE_MODEL = ConfigManager()
LARGE_MODEL.model_config = ModelConfig(
num_classes=80,
num_queries=200,
num_frames=5,
backbone_depth=101, # ResNet-101
hidden_dim=512,
num_heads=16,
)
LARGE_MODEL.training_config.batch_size = 1
LARGE_MODEL.training_config.learning_rate = 5e-5
# Quick start examples
QUICK_START_GUIDE = """
╔════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ DVIS++ Quick Start Guide ║
╚════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
1. INSTALLATION
pip install torch torchvision
cd dvis_plus_plus
pip install -r requirements.txt
2. BASIC USAGE (5 minutes)
from dvis_pp import DVISPlusPlus
import torch
# Create model
model = DVISPlusPlus(num_classes=80)
# Create dummy input (5 frames)
frames = [torch.randn(1, 3, 512, 512) for _ in range(5)]
# Inference
outputs = model(frames)
3. TRAINING (30 minutes setup)
python main.py --mode train \\
--data-dir /path/to/videos \\
--anno-file /path/to/annotations.json \\
--num-epochs 100 \\
--batch-size 2
4. INFERENCE (5 minutes)
python main.py --mode inference \\
--video-path /path/to/video.mp4 \\
--checkpoint /path/to/checkpoint.pt \\
--output-dir ./output
5. EVALUATION (10 minutes)
python main.py --mode evaluate \\
--data-dir /path/to/videos \\
--anno-file /path/to/annotations.json \\
--checkpoint /path/to/checkpoint.pt
6. OPEN-VOCABULARY SEGMENTATION
from dvis_pp import DVISPlusPlusWithClip
model = DVISPlusPlusWithClip(clip_model_name='ViT-B/32')
class_names = ['person', 'dog', 'car', ...]
outputs = model.forward_ov(frames, class_names)
CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES:
Small Model (Fast, less memory):
- Backbone: ResNet-18
- Queries: 50
- Frames: 3
- Batch Size: 4
Medium Model (Balanced):
- Backbone: ResNet-50
- Queries: 100
- Frames: 5
- Batch Size: 2
Large Model (Best quality, more memory):
- Backbone: ResNet-101
- Queries: 200
- Frames: 5
- Batch Size: 1
TROUBLESHOOTING:
Out of Memory:
- Reduce batch size
- Reduce image size
- Reduce num_frames
- Use smaller backbone
Slow Training:
- Use fewer frames
- Reduce image resolution
- Increase num_workers
Poor Results:
- Train longer (more epochs)
- Check dataset format
- Adjust learning rate
- Use data augmentation
For more information, see README.md
"""
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Print quick start guide
print(QUICK_START_GUIDE)
# Save example configurations
print("\nSaving example configurations...")
config_dir = Path('./configs')
config_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
SMALL_MODEL.save(str(config_dir / 'small.json'))
MEDIUM_MODEL.save(str(config_dir / 'medium.json'))
LARGE_MODEL.save(str(config_dir / 'large.json'))
print("✓ Configurations saved to ./configs/")
# Print configurations
print("\n" + "="*80)
print("PRESET CONFIGURATIONS")
print("="*80)
print(SMALL_MODEL)
print(MEDIUM_MODEL)
print(LARGE_MODEL)Related posts, You May like to read
- 7 Shocking Truths About Knowledge Distillation: The Good, The Bad, and The Breakthrough (SAKD)
- MOSEv2: The Game-Changing Video Object Segmentation Dataset for Real-World AI Applications
- MedDINOv3: Revolutionizing Medical Image Segmentation with Adaptable Vision Foundation Models
- HiPerformer: A New Benchmark in Medical Image Segmentation with Modular Hierarchical Fusion
- GeoSAM2 3D Part Segmentation — Prompt-Controllable, Geometry-Aware Masks for Precision 3D Editing
- SegTrans: The Breakthrough Framework That Makes AI Segmentation Models Vulnerable to Transfer Attacks
- Universal Text-Driven Medical Image Segmentation: How MedCLIP-SAMv2 Revolutionizes Diagnostic AI
- Towards Trustworthy Breast Tumor Segmentation in Ultrasound Using AI Uncertainty
- Cellpose3: The Revolutionary One-Click Solution for Restoring Noisy, Blurry, and Undersampled Microscopy Images

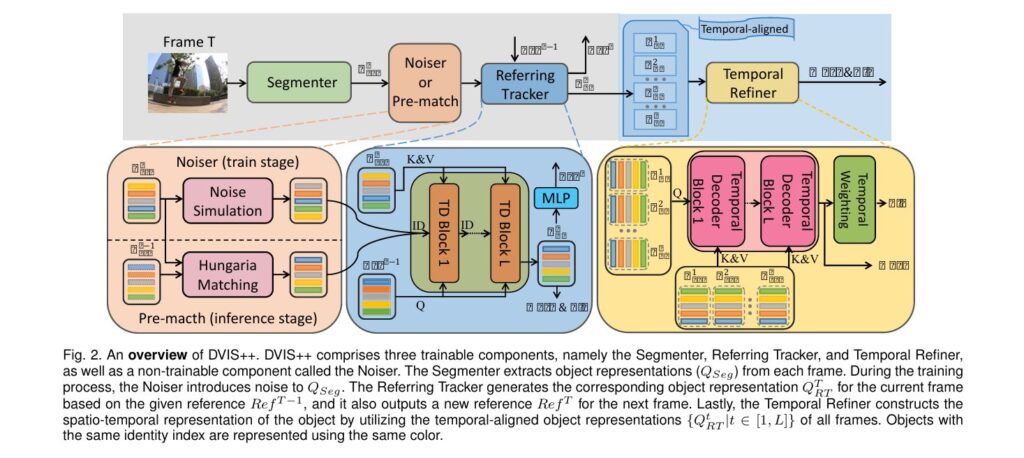
Pingback: Revolutionizing Medical Imaging: How a Compact, Programmable Ultrasound Array Unlocks High-Contrast Elastography for Bones and Tumors - aitrendblend.com